About electrical protection devices for "dummies": residual current device (RCD)
 Imagine the following - a washing machine is installed in your bathroom. Whatever the well-known brand, devices of any manufacturer are subject to breakdown, and, say, the most banal thing happens - the insulation on the power cord is damaged and the network potential is on the machine body. And this is not even a breakdown, the car continues to work, but it is already becoming a source of increased danger. After all, if we touch both the car body and the water pipe at the same time, we will close the electric circuit through ourselves. And in most cases it will be fatal.
Imagine the following - a washing machine is installed in your bathroom. Whatever the well-known brand, devices of any manufacturer are subject to breakdown, and, say, the most banal thing happens - the insulation on the power cord is damaged and the network potential is on the machine body. And this is not even a breakdown, the car continues to work, but it is already becoming a source of increased danger. After all, if we touch both the car body and the water pipe at the same time, we will close the electric circuit through ourselves. And in most cases it will be fatal.
To avoid these terrible consequences, RCDs were invented - protective shutdown devices.
An UZO is a high-speed protective switch that responds to differential current in conductors that supply electricity to the protected electrical installation - this is the "official" definition. In a more understandable language, the device will disconnect the consumer from the mains supply if a current leakage occurs to the PE (ground) conductor. Let's consider the principle of operation of the RCD ...
How to make a simple status indicator of a remote lamp
 At one time, I was faced with the need to control the burning and integrity of the light bulb when the switch is in another room (for example, a basement, cellar or chicken coop). More than once it happened, the switch is turned on, and the light does not light up: it either burned out, or the contact in the cartridge or switch disappeared. In this case, the switch is located in the corridor, and to the basement, where hens live, you need to go around the house. It is especially bad when, because of this, the bird does not enter the basement in the evening, and then it must be entered manually. The problem was solved by installing a simple and trouble-free device that indicates the flow of current in the circuit of the lighting lamp and is located near the switch.
At one time, I was faced with the need to control the burning and integrity of the light bulb when the switch is in another room (for example, a basement, cellar or chicken coop). More than once it happened, the switch is turned on, and the light does not light up: it either burned out, or the contact in the cartridge or switch disappeared. In this case, the switch is located in the corridor, and to the basement, where hens live, you need to go around the house. It is especially bad when, because of this, the bird does not enter the basement in the evening, and then it must be entered manually. The problem was solved by installing a simple and trouble-free device that indicates the flow of current in the circuit of the lighting lamp and is located near the switch.
The indicator diagram is shown in the figure. When current flows through ballast diodes, a voltage sufficient for the LED to glow is incident on them. You can connect the device at any convenient point in the electrical circuit (before or after the switch) or to break the second wire leading to the lamp.
The indicator is not critical to details. As ballast diodes, you can use any small-sized diodes with an allowable direct current not lower than the current consumption of the illuminator and any operating voltage ...
In the near future, all power cables will be made of superconducting materials
 The flow of current in conductors is always associated with energy losses, i.e. with the transition of energy from electrical to thermal. This transition is irreversible, the reverse transition is associated only with the completion of work, as thermodynamics speaks of this. There is, however, the possibility of converting thermal energy into electrical energy and using the so-called thermoelectric effect, when two contacts of two conductors are used, one of which is heated and the other is cooled.
The flow of current in conductors is always associated with energy losses, i.e. with the transition of energy from electrical to thermal. This transition is irreversible, the reverse transition is associated only with the completion of work, as thermodynamics speaks of this. There is, however, the possibility of converting thermal energy into electrical energy and using the so-called thermoelectric effect, when two contacts of two conductors are used, one of which is heated and the other is cooled.
In fact, and this fact is surprising, there are a number of conductors in which, under certain conditions, there is no energy loss during the flow of current! In classical physics, this effect is inexplicable.
According to the classical electronic theory, the motion of a charge carrier occurs in an electric field uniformly accelerated until it collides with a structural defect or with a lattice vibration. After a collision, if it is inelastic, like a collision of two plasticine balls, an electron loses energy, transferring it to a lattice of metal atoms. In this case, in principle, there can be no superconductivity.
It turns out that superconductivity appears only when quantum effects are taken into account. It’s hard to imagine it.A slight idea of the mechanism of superconductivity can be obtained from the following considerations ...
About electrical protection devices for dummies: circuit breakers
 Many people remember Soviet circuit breakers - plugs. Instead of ordinary ceramic plugs, they were screwed into the shield of an electric meter. It was a compromise solution, which, in general, paid off. Indeed, thanks to this, plugs became "reusable", and without changing the existing design of the electrical panel. In general, the inventor of automatic protection devices is ABB, which patented a small-sized circuit breaker in 1923. Much time has passed since then, but the principle of operation of the circuit breaker has remained unchanged - the restoration of its normal operation with one movement of the hand.
Many people remember Soviet circuit breakers - plugs. Instead of ordinary ceramic plugs, they were screwed into the shield of an electric meter. It was a compromise solution, which, in general, paid off. Indeed, thanks to this, plugs became "reusable", and without changing the existing design of the electrical panel. In general, the inventor of automatic protection devices is ABB, which patented a small-sized circuit breaker in 1923. Much time has passed since then, but the principle of operation of the circuit breaker has remained unchanged - the restoration of its normal operation with one movement of the hand.
A circuit breaker is a switching electrical apparatus designed to conduct current in normal conditions and to automatically turn off electrical installations when short-circuit currents and overloads occur. The most common and popular today are circuit breakers that are mounted on a 35 mm DIN rail in a distribution panel.
The main parameter of circuit breakers is the rated current. This is a current whose value in a particular circuit is considered normal, i.e. for which electrical equipment is designed. For electrical installations in residential buildings, the rated current ...
How plants respond to electricity
 To begin with, the agricultural industry is completely destroyed. What's next? Is it time to collect stones? Is it time to unite all the creative forces to give the villagers and summer residents those new products that will dramatically increase productivity, reduce manual labor, find new ways in genetics ... I would suggest readers of the magazine to be authors of the heading "For the village and summer residents". I will start with the long-standing work "Electric field and productivity."
To begin with, the agricultural industry is completely destroyed. What's next? Is it time to collect stones? Is it time to unite all the creative forces to give the villagers and summer residents those new products that will dramatically increase productivity, reduce manual labor, find new ways in genetics ... I would suggest readers of the magazine to be authors of the heading "For the village and summer residents". I will start with the long-standing work "Electric field and productivity."
In 1954, when I was a student of the Military Academy of Communications in Leningrad, I was passionately carried away by the process of photosynthesis and conducted an interesting test with growing onions on the windowsill. The windows of the room in which I lived were facing north, and therefore the bulbs could not receive the sun. I planted five bulbs in two elongated boxes. He took the earth in the same place for both boxes. I had no fertilizers, i.e. the same conditions for growing were created. Above one box on top, at a distance of half a meter (Fig. 1), I placed a metal plate to which I attached a wire from a high-voltage rectifier + 10 000 V, and a nail was inserted into the ground of this box, to which I connected a “-” wire from the rectifier.
I did this so that, according to my theory of catalysis, the creation of high potential in the plant zone will lead to an increase in the dipole moment of the molecules involved in the photosynthesis reaction, and the test days are drawn. Within two weeks I discovered ...
About electrical protection devices for "dummies": fuses
 Fuses are designed to protect electrical networks from overloads and short circuits. They are very cheap and elementary simple in design. These devices are rightfully considered pioneers of circuit protection.
Fuses are designed to protect electrical networks from overloads and short circuits. They are very cheap and elementary simple in design. These devices are rightfully considered pioneers of circuit protection.
The fuse consists of two main parts: the casing is made of electrical insulating material (glass, ceramics) and the fuse (wire, metal strips). The outputs of the fuse-link are connected to the terminals, with the help of which the fuse is connected in series with the protected consumer or the circuit section. To do this, use special terminal holders. They must ensure reliable contact of the fuse - otherwise heating is possible in this place.
The fusible insert is selected so that it melts before the temperature of the line wires reaches a dangerous level or an overloaded consumer fails.
By design features distinguish between plate, cartridge, tube and plug fuses. The current strength for which the fuse is designed is indicated on its body. The maximum permissible voltage at which a fuse can be used is also specified.
The main characteristic of the fusible insert is the dependence of the time of its burnout on the current. This dependency is the following graph ...
How to easily control a powerful AC load
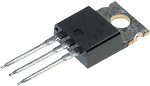 Sometimes you need a weak signal from the microcontroller to turn on a powerful load, such as a lamp in the room. This problem is especially relevant for smart home developers. The first thing that comes to mind is a relay. But do not rush, there is a better way :)
Sometimes you need a weak signal from the microcontroller to turn on a powerful load, such as a lamp in the room. This problem is especially relevant for smart home developers. The first thing that comes to mind is a relay. But do not rush, there is a better way :)
In fact, the relay is a continuous hemorrhage. Firstly, they are expensive, and secondly, to power the relay coil, an amplifying transistor is needed, since the weak leg of the microcontroller is not capable of such a feat. Well, and thirdly, any relay is a very bulky design, especially if it is a power relay designed for high current.
If we are talking about alternating current, then it is better to use triacs or thyristors. What it is? And now I’ll tell you.
If on the fingers, then the thyristor is similar to a diode, even the designation is similar. Passes current in one direction and does not let in the other. But he has one feature that distinguishes it from the diode radically - the control input.
If the opening current is not applied to the control input, the thyristor will not pass current even in the forward direction. But it is worth giving at least a brief impulse, as it immediately opens and remains open as long as there is direct voltage. If the voltage is removed or polarity reversed, the thyristor will close ...
Home-made device for protecting the motor from under-phase conditions and overload
 As typical elements of motor protection, electrothermal relays are most often used. Designers are forced to overestimate the rated current of these relays, so that there are no trips at startup. The reliability of such protection is low, and a large percentage of engines fail during operation.
As typical elements of motor protection, electrothermal relays are most often used. Designers are forced to overestimate the rated current of these relays, so that there are no trips at startup. The reliability of such protection is low, and a large percentage of engines fail during operation.
The circuit of the motor protection device (see the figure) from out-of-phase modes and overload is characterized by increased reliability. Transistors VT1, VT2 together with the elements connected to them form an analog of a dynistor, the switching voltage of which (Uin) depends on the ratio R6 / R7. With the ratings indicated on the diagram 30 V < Uon <36 V in the temperature range -15 Resistors R1 ... R3 form a vector adder, at the output of which the voltage is 0, if the motor is full-phase. The transformer T1 is a current sensor of one phase of the electric motor. The outputs of the current sensor and vector adder are connected to a rectifier made on diodes VD1 ... VD3. In normal mode, the voltage at the rectifier output is determined by the current in the primary winding T1 and the ratio of turns wl / w2. Using a resistor R4, this voltage is set below U on VT1 and VT2. If phase failure or motor overload occurs, then ...
How not to spoil your health in the pursuit of energy savings
 In the literature, there is always a theme of saving electricity and extending the life of incandescent lamps. In most articles, a very simple method is proposed - switching a semiconductor diode in series with the lamp.
In the literature, there is always a theme of saving electricity and extending the life of incandescent lamps. In most articles, a very simple method is proposed - switching a semiconductor diode in series with the lamp.
This topic has repeatedly appeared in the magazines "Radio", "Radio amateur", she did not bypass "Radioamator" [1-4]. They offer a variety of solutions: from the simple inclusion of a diode in series with a cartridge [2], the difficult manufacture of a “tablet” [1] and the “prescribing an aspirin bulb” [3] to the manufacture of a “base adapter” [4].At the same time, a quiet debate erupts on the pages of Radioamator about whose tablet is better and how to swallow it.
The authors took good care of the "health" and "durability" of the incandescent lamp and completely forgot about their health and the health of their family. "What's the matter?" - you ask. Just in those blinks that suggest masking with the help of a “milky” lampshade [3]. There may be an illusion of a decrease in blinks, but this will not make them smaller, and their negative impact will not decrease.
So, we can choose which is more important: the health of the light bulb or ours? Is natural light better than artificial? Of course! Why? There can be many answers. And one of them - artificial lighting, for example, incandescent lamps, blinks at a frequency of 100 Hz. Pay attention not to 50 Hz, as it is sometimes mistakenly believed, referring to the frequency of the electrical network. Due to the inertia of our vision, we do not notice flashes, but this does not mean at all that we do not perceive them. They affect the organs of vision and, of course, the human nervous system. We get tired faster ...

Despite the indisputable successes of the modern theory of electromagnetism, the creation on its basis of such directions as electrical engineering, radio engineering, electronics, there is no reason to consider this theory complete.
The main drawback of the existing theory of electromagnetism is the lack of model concepts, a lack of understanding of the essence of electrical processes; hence the practical impossibility of further development and improvement of the theory. And from the limitations of the theory, many applied difficulties also follow.
There are no grounds for believing the theory of electromagnetism to be the height of perfection. In fact, the theory has accumulated a number of omissions and direct paradoxes for which very unsatisfactory explanations have been invented, or there are no such explanations at all.
For example, how to explain that two mutually motionless identical charges, which are supposed to be repelled from each other according to the Coulomb law, are actually attracted if they move together a relatively long-abandoned source? But they are attracted, because now they are currents, and identical currents are attracted, and this has been experimentally proved.
Why does the electromagnetic field energy per unit length of a conductor with the current generating this magnetic field tend to infinity if the return conductor is moved away? Not the energy of the entire conductor, but precisely per unit length, say, one meter? ...
What you need to know when installing an RCD and grounding device in an apartment or private house
 It is not necessary to use RCDs or electronically controlled difavtomats, for example, IEK AD 12, IEK AD 14 diflavtomats, when the phase or neutral conductor breaks, the power of the electronic control circuit is de-energized and the differential protection stops working. There is a diffrel with an electronic control circuit in which, in the event of a power failure, the consumer shuts down in the likeness of a starter. To connect the consumer after resuming power, you must manually turn on this type of diffrel. This type of differential switch can be used to power electrical appliances where it is dangerous to re-supply voltage after a power failure.
It is not necessary to use RCDs or electronically controlled difavtomats, for example, IEK AD 12, IEK AD 14 diflavtomats, when the phase or neutral conductor breaks, the power of the electronic control circuit is de-energized and the differential protection stops working. There is a diffrel with an electronic control circuit in which, in the event of a power failure, the consumer shuts down in the likeness of a starter. To connect the consumer after resuming power, you must manually turn on this type of diffrel. This type of differential switch can be used to power electrical appliances where it is dangerous to re-supply voltage after a power failure.
With improperly made grounding can be more dangerous than without grounding !!!
Grounding without an RCD or grounding is prohibited !!!
Do not connect the ground terminals of outlets and electrical appliances protected only by circuit breakers that protect only wiring from short circuits in the phase-neutral and phase-phase circuits, to natural, artificial and especially home-made grounding. You expose yourself and others to mortal danger. Automata are triggered only by currents many times higher than the nominal value of the automaton.Natural, artificial and especially home-made grounding in the vast majority of cases has a resistance that cannot create such currents and, accordingly, carry out a protective shutdown of automatic machines within 0.4 seconds normalized by safety ...
To the history of electric lighting
 This story begins with a topic very far from electricity, which confirms the fact that in science there are no secondary or unpromising for study. In 1644 Italian physicist E. Toricelli invented the barometer. The device was a glass tube about a meter long with a sealed end. The other end was dipped in a cup of mercury. In the tube, the mercury did not sink completely, but the so-called “Toricellian emptiness” formed, the volume of which changed due to weather conditions.
This story begins with a topic very far from electricity, which confirms the fact that in science there are no secondary or unpromising for study. In 1644 Italian physicist E. Toricelli invented the barometer. The device was a glass tube about a meter long with a sealed end. The other end was dipped in a cup of mercury. In the tube, the mercury did not sink completely, but the so-called “Toricellian emptiness” formed, the volume of which changed due to weather conditions.
In February 1645 Cardinal Giovanni de Medici ordered that several such pipes be installed in Rome and kept under surveillance. This is surprising for two reasons. Toricelli was a student of G. Galileo, who in recent years has been disgraced for atheism. Secondly, a valuable idea followed from the Catholic hierarch and since then barometric observations began ...
