Categories: Featured Articles » Sources of light
Number of views: 17817
Comments on the article: 0
Light distribution curves
The light distribution curves of luminaires are one of their most important parameters, along with the ratio of light fluxes distributed in the lower and upper hemispheres.
A lamp as a lighting device is not manufactured for one object, therefore, even at the design stage, a lamp is developed as a standard one, which can be used massively in many places.
Here, one of the key points is the distribution of the light flux in space, which determines where this lamp can be used and where it is not possible, in accordance with GOST 17677-82 “Lamps, general technical conditions”.

The first thing to understand is that the light distribution curve can be symmetric or asymmetric, and there are seven main types of symmetrical (most common) light fluxes, which depends on the shape of the light distribution curve of the lamp.
Each type has its own directivity zone, which is measured in degrees, depending on the angle of the light flux. So, light curves are of the following seven types:
-
Concentrated (K) - 30 °;
-
Deep (G) - 60 °;
-
Cosine (D) - 120 °;
-
Half-wide (L) - 140 °;
-
Wide (W) - 160 °;
-
Uniform (M) - 180 °;
-
Sinus (C) - 90 °.
Typical curves are idealized, and in reality light distribution curves may differ from them, however, the general nature of the curves must comply with the standard ones, according to the requirements of GOST or SNiP. To compare the parameters of the curves of the distribution of light intensity, a light source is taken, given by the luminous flux (possibly total) of 1000 Lumens.
Each type of room or landscape has its own form of light distribution curve.
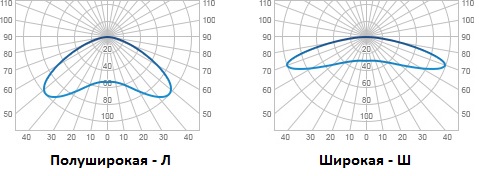
Streets and motorways, the category of which is determined according to SNiP 23-05-05, transport tunnels, underground and elevated pedestrian crossings, long corridors of public buildings, should be illuminated with luminaires with a “half-wide” or “wide” shape of the light intensity curve.
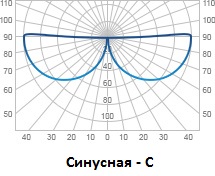
For halls of buildings where you need to get a muffled or reflected light, it is best to use reflected light fixtures with a "sinus" light intensity curve.
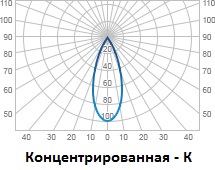
If we are talking about highlighting a selected area, a special internal architectural composition or an unusual interior detail, a lighting device with a “concentrated” light curve is suitable.
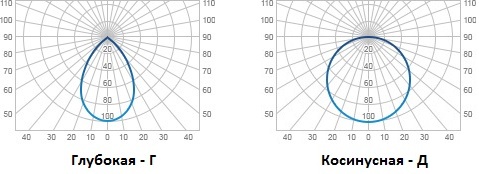
Industrial premises are illuminated by luminaires with “concentrated”, “deep” or “cosine” light distribution curves. And the higher the lighting device is suspended, the narrower the maximum light zone will be. Offices are traditionally lit with scattered or direct light fixtures with "deep" and "cosine" curves.
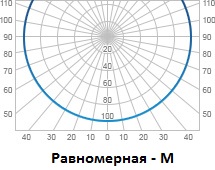
Utility rooms, cabins, porches, illuminate fixtures with a "uniform" curve.
In addition, the luminaires are also classified by the type of luminous flux, in accordance with the fraction of the luminous flux, which falls directly on the lower hemisphere:
-
Direct light (P) - more than 80%;
-
Mostly direct light (H) - from 60 to 80%;
-
Scattered light (P) - from 40 to 60%;
-
Mostly reflected light (B) - from 20 to 40%;
-
Reflected light (O) - up to 20%.
Direct light fixtures are mainly used in rooms where ceilings are not very high. Often, these lights are quite economical recessed or conventional pendant lights. They are well suited for lighting interior elements: statues, paintings. Convenient for lighting your desktop or reading place.
The scattered light fixtures are good for general lighting. They give uniform saturated light of distributed brightness and soft shadows.Such lighting is quite comfortable for vision and for the human nervous system.
The luminaires of the reflected light give a comfortable uniform light, saturated, which at the same time does not blind. It goes well with daylight.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
