Categories: Interesting Facts, Interesting electrical news
Number of views: 53539
Comments on the article: 4
The most interesting thing about trains on a magnetic suspension
 Magnetoplan or Maglev (from English magnetic levitation) is a train on a magnetic suspension, driven and controlled by magnetic forces. Such a composition, unlike traditional trains, does not touch the rail surface during movement. Since there is a gap between the train and the surface of movement, friction is eliminated, and the only drag force is the force of aerodynamic drag.
Magnetoplan or Maglev (from English magnetic levitation) is a train on a magnetic suspension, driven and controlled by magnetic forces. Such a composition, unlike traditional trains, does not touch the rail surface during movement. Since there is a gap between the train and the surface of movement, friction is eliminated, and the only drag force is the force of aerodynamic drag.
The speed achievable by the Muggle is comparable to the speed of the aircraft and allows you to compete with air traffic at small (for aviation) distances (up to 1000 km). Although the idea of such a transport is not new, economic and technical limitations did not allow it to unfold fully: for public use, the technology was implemented only a few times. Currently, Maglev can not use the existing transport infrastructure, although there are projects with the location of the elements of the magnetic road between the rails of a conventional railway or under the track.
Magnetic Suspension Train Overview
At the moment, there are 3 main technologies for magnetic suspension of trains:
1. On superconducting magnets (electrodynamic suspension, EDS).
Superconducting magnet - a solenoid or electromagnet with a winding of superconducting material. A winding in a state of superconductivity has zero ohmic resistance. If such a winding is short-circuited, then the electric current induced in it is maintained for almost any time.
The magnetic field of the undamped current circulating through the winding of the superconducting magnet is extremely stable and free of ripples, which is important for a number of applications in scientific research and technology. The winding of a superconducting magnet loses its superconductivity property when the temperature rises above the critical temperature Tk of the superconductor, when the critical current Ik or critical magnetic field Hk reaches the winding. Given this, for windings of superconducting magnets. apply materials with high values of Tk, Ik and Nk.
2. On electromagnets (electromagnetic suspension, EMS).
3. On permanent magnets; it is a new and potentially the most economical system.
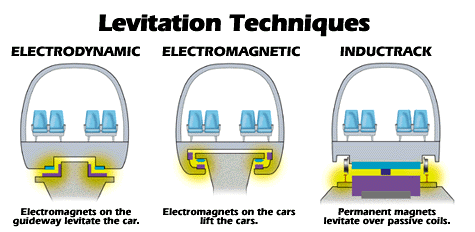
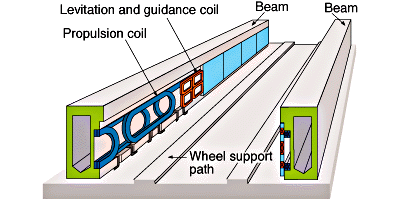
The composition levitates due to the repulsion of the same poles of magnets and, conversely, the attraction of different poles. The movement is carried out by a linear motor.
Linear motor — an electric motor in which one of the elements of the magnetic system is open and has an expanded winding that creates a traveling magnetic field, and the other is made in the form of a guide providing linear movement of the moving part of the motor.
Nowadays, many linear engine projects have been developed, but all of them can be divided into two categories - low acceleration engines and high acceleration engines.
Low acceleration engines are used in public transport (maglev, monorail, subway). High acceleration engines are very small in length, and are usually used to accelerate an object to high speed and then release it. They are often used for research on hyper-velocity collisions, like weapons or spacecraft launchers. Linear motors are also widely used in feed drives of metal cutting machines, and in robotics. located either on the train, or on the way, or both there and there. A serious design problem is the large weight of sufficiently powerful magnets, since a strong magnetic field is required to maintain a massive composition in the air.
By the Earnshaw theorem (sometimes written by Earnshaw), static fields created by electromagnets and permanent magnets alone are unstable, unlike diamagnetics fields.
Diamagnets - substances that are magnetized in the direction of the external magnetic field acting on them. In the absence of an external magnetic field, diamagnets do not have a magnetic moment. and superconducting magnets. There are stabilization systems: sensors constantly measure the distance from the train to the track and, accordingly, the voltage on the electromagnets changes. The most active Muggle developments are Germany and Japan.
Advantages
-
Theoretically, the highest speed that can be obtained on serial (not sports) ground transport.
-
Low noise.
disadvantages
-
The high cost of creating and maintaining a gauge.
-
Weight of magnets, power consumption.
-
The electromagnetic field created by the magnetic suspension may be harmful to train crews and / or surrounding residents. Even traction transformers used on railways electrified with alternating current are harmful for drivers, but in this case the field strength is an order of magnitude greater. It is also possible that muggle lines will not be available to people using pacemakers.
-
It will be required at high speed (hundreds of km / h) to control the gap between the road and the train (several centimeters). This requires ultra-fast control systems.
-
Complex travel infrastructure is required.
For example, the arrow for the Muggle is two sections of the road that replace each other depending on the direction of rotation. Therefore, it is unlikely that Muggle lines will form more or less branched networks with forks and intersections.
Options
There are projects of magnetic roads with various types of magnetic suspension, for example, Tubular Rail offers to abandon the rail as such, and use only periodically spaced annular supports.
Implementation
M-Bahn in Berlin
The first public Muggle system (M-Bahn) was built in Berlin in the 1980s.
A 1.6 km long road connected 3 metro stations from the Gleisdreieck railway junction to the Potsdamer Strasse exhibition grounds. After long trials, the road was open for passenger traffic on August 28, 1989. The journey was free, the cars were controlled automatically without a driver, the road worked only on weekends. In the area where the road approached, it was supposed to carry out mass construction. The road was built on the trestle of the former U2 metro line, where traffic was interrupted due to the division of Germany and the destruction during the war. July 18, 1991 the line went into commercial operation and is included in the Berlin metro system.
After the destruction of the Berlin Wall, the population of Berlin actually doubled and it was necessary to connect the transport networks of East and West. The new road interrupted an important metro line, and the city needed to ensure high passenger traffic. 13 days after putting into commercial operation, on July 31, 1991, the municipality decided to dismantle the magnetic road and restore the metro. On September 17, the road was dismantled, and later, the metro was restored.

Birmingham
A speedy muggle shuttle ran from Birmingham Airport to the nearest train station between 1984 and 1995. The length of the route was 600 m, and the suspension gap was 1.5 cm. The road, having worked for 10 years, was closed due to passenger complaints about inconvenience and was replaced by a traditional monorail.
Shanghai
The failure with the first Muggle road in Berlin did not deter the German company Transrapid, a subsidiary of Siemens AG and ThyssenKrupp, from continuing to research, and later the company received an order from the Chinese government to build a high-speed (450 km / h) Muggle line from Shanghai Pudong Airport to Shanghai. The road was opened in 2002, its length is 30 km. In the future, it is planned to extend it to the other end of the city to the old Hongqiao Airport and further southwest to Hangzhou, after which its total length should be 175 km.
Japan
In Japan, a road is being tested in the vicinity of Yamanashi Prefecture using JR-Maglev technology. The speed achieved during tests with the MLX01-901 with passengers on December 2, 2003 was 581 km / h.
There, in Japan, a new track was put into commercial operation at the opening of Expo 2005 in March 2005. The 9 km Linimo (Nagoya) line consists of 9 stations. The minimum radius is 75 m, the maximum slope is 6%. The linear engine allows the train to accelerate to 100 km / h in seconds. The line serves the area adjacent to the venue, Aichi University, and some parts of Nagakute. Trains manufactured by Chubu HSST Development Corp.
There is evidence that the above Japanese companies are building a similar line in South Korea.
Japan will launch a magnetic cushion train
Japan plans to launch an ultra-fast magnetic cushion train in fiscal year 2025. The construction of the line and trains will cost about $ 45 billion, AFP reports.
The train will use magnetic levitation technology (sometimes called muggle). A magnetic field allows the composition, despite the Earth's gravity, to soar above the line and due to this move much faster than a regular train.
The world's only operating passenger magnetic-levitation railway line is located in Shanghai and has a length of 30.5 kilometers. The train moves along it at a speed of 430 kilometers per hour.
A 290-kilometer Japanese line will connect Tokyo and the as-yet-undefined area in central Japan. It is expected that trains with a linear electric motor will reach speeds of about 500 kilometers per hour.
The construction of the line will be undertaken by the Central Japan Railway Co. (JR Central), which in 2003 already tested magnetic levitation technology. The experienced team then set a world speed record for the train: 581 kilometers per hour. Recall that the speed record for a conventional rail train belongs to France - 574.8 kilometers per hour.
The company will spend about $ 45 billion on the project. Initially, it was expected that the government partially subsidized the construction of the line, but these hopes did not materialize, as a result, the company will find funds by increasing its long-term debt. Jr-maglev
JR-Maglev uses electrodynamic suspension with superconducting magnets (EDS), installed both on the train and on the track. Unlike the German Transrapid system (operating line from Shanghai to Shanghai Airport in China), JR-Maglev does not use a monorail scheme: trains move in the channel between the magnets. Such a scheme allows you to develop higher speeds, provides greater passenger safety in case of evacuation and ease of operation.
The movement of the maglev is due to the linear motor.
Unlike electromagnetic suspension (EMS), trains created using EDS technology require additional wheels when driving at low speeds (up to 150 km / h). When a certain speed is reached, the wheels are separated from the ground and the train “flies” at a distance of several centimeters from the surface. In the event of an accident, the wheels also allow a softer stop of the train. However, at the cost of building and operating the EDS system implemented by JR-Maglev is more expensive than EMS Transrapid systems.
For braking in normal mode, electrodynamic brakes are used. For emergency cases, the train is equipped with retractable aerodynamic and disc brakes on carts.
On the line in Yamanashi, several trains with different shapes of the nose fairing are being tested: from the usual pointed, to almost flat, 14 meters long, designed to get rid of the loud cotton that accompanies the train entering the tunnel at high speed. A Muggle train can be fully computer controlled.The driver monitors the operation of the computer and receives an image of the path through the video camera (the driver’s cab does not have front-view windows).
The Chinese against the "road of the future"
The population of Shanghai has come out with mass protests against local pride - a unique magnetic cushion railway, whose trains seem to fly through the air.
Moreover, it was not half-starved workers who took to the streets, but rather well-off middle-class representatives. They violated the country's ban on demonstrations and chanted: “Save the children, resist radiation!”
Powerful magnets, as it were, hang the train over the platform and push it forward at a speed of up to 430 kilometers per hour. For the launch of the first route - from the airport to the city outskirts - $ 1.4 billion was paid, and now in Shanghai they decided to extend this road another 30 kilometers further through the city.
“We feel like we live in a microwave, our homes have depreciated, realtors refuse to deal with us when they find out that our homes are near the train route,” complain the Chinese, whose homes were in close proximity to the “road of the future” " According to them, the highway emits a strong electromagnetic radiation.
The “railway of the future” created in Germany, and previously caused protests from the people of Shanghai. But this time, the authorities, frightened by demonstrations threatening to spill over into major unrest, promised to deal with trains. In order to stop the demonstrations in time, officials even hung up video cameras in those places where mass protests most often took place. The Chinese crowd is very organized and mobile, it can gather in a matter of seconds and turn into a demonstration with slogans.
These are the largest folk performances in Shanghai since the anti-Japanese marches in 2005. This is not the first protest caused by the Chinese concern over the worsening environment. Last summer, thousands of demonstrators forced the government to postpone the construction of a chemical complex.
A comment
According to WWF ecologists, the biggest danger from magnetic cushion trains is the so-called noise pollution. The noise of these trains is much more unpleasant and annoying than that of conventional trains or trains. Constant stay in the area of this noise causes a feeling of anxiety, insecurity, irritation. Any sounds in one way or another act on people annoyingly, and these especially, experts emphasize. Problems with radiation, magnetic or thermal, are usually not observed, because such trains run for short distances and with large time intervals.
See also: Minato Magnetic Motor
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
