Categories: Featured Articles » Interesting Facts
Number of views: 4134
Comments on the article: 0
Superconducting magnets
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet whose winding has the property of a superconductor. As in any electromagnet, the magnetic field is generated here by direct current flowing through the winding wire. But since the current passes in this case not through an ordinary copper conductor, but through a superconductor, the active losses in such a device will be extremely small.
As superconductors for magnets of this type, superconductors of the second kind almost always act, that is, those in which the dependence of magnetic induction on the strength of the longitudinal magnetic field is nonlinear.
In order for a superconducting magnet to begin to show its properties, ordinary conditions are not enough - it must be brought to a low temperature, which in principle can be achieved in various ways. The classic way is this: the device is placed in a Dewar vessel with liquid helium, and the Dewar vessel with liquid helium itself is placed inside another Dewar vessel, with liquid nitrogen, so that liquid helium evaporates as low as possible.
As a real example of a powerful superconducting magnet, we can use the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) magnet, in which, using the strongest magnetic field it is necessary to keep high-energy protons flying at an incredible speed on a certain trajectory inside an extended underground tunnel.
1232 huge electromagnets, each weighing about 30 tons, and has a length of 15 meters, are installed in the tunnel of the LHC one after another. Proton beams pass here through thin tubes, and these tubes just pass inside dipole magnets, the magnitude of the induction of which is regulated in the range from 0.54 to 8.3 T.
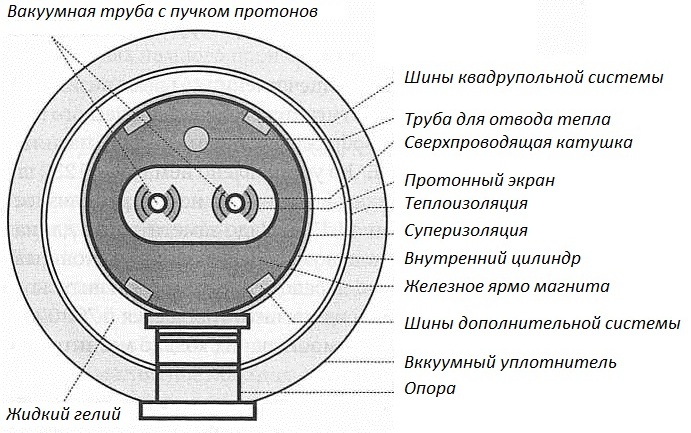
The superconducting properties of magnets on the LHC are achieved by using a special superconducting wire: each magnetic dipole contains an individual superconducting coil wound with a niobium-titanium cable, and the cable itself is composed of the thinnest wires with a diameter of 6 microns.
The bottom line is that niobium-titanium is a low-temperature superconductor, so the temperature required to maintain the nominal superconductivity of such windings is here only 1.9 K (lower than the temperature of the background microwave radiation in outer space).
The LHC magnet cooling system works thanks to liquid helium, which is constantly in motion. 97 tons of liquid helium are located inside a special shell where superfluidity of this coolant is achieved under a certain pressure.
Direct cooling of liquid helium occurs under the influence of 10,000 tons of liquid nitrogen. The cooling process is carried out in two stages: a conventional type freezer first cools helium to 4.5K, and then it is additionally cooled, but already under reduced pressure. All this action takes about a month.
When the conditions regarding temperature are ensured, the turn of huge currents sets in. On the LHC, the magnets supply current reaches 12,000 amperes. At the same time, power is consumed, comparable to that accounted for by the power supply of the entire city of Geneva. The electrical energy per superconducting magnet is approximately 10 MJ.

Superconducting magnets are also used in NMR tomographs and spectrometers, in magnetic cushion trains, in thermonuclear reactors, and in many other experimental installations, for example associated with levitation.
An interesting fact: weak diamagnetic fields practically do not have any tangible effect on diamagnetics, but when it comes to strong magnetic fields generated by superconducting magnets, the picture here changes significantly.Carbon entering into organic objects and living organisms is a diamagnet, so a living frog can soar in a magnetic field with an induction of 16 T.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
