Categories: Interesting Facts, Novice electricians
Number of views: 73956
Comments on the article: 0
Boolean algebra. Part 1. A bit of history
 At school, we all studied algebra, but they did not talk about Boolean algebra there. What is the difference between Boolean algebra and school algebra, the history of its appearance, problems and applications are described in this article.
At school, we all studied algebra, but they did not talk about Boolean algebra there. What is the difference between Boolean algebra and school algebra, the history of its appearance, problems and applications are described in this article.
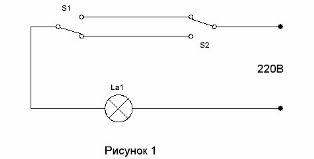
The circuit that allows two switches to turn on the light in the corridor at the entrance to the corridor and turn it off when entering the room has been known for a very long time (see. Corridor Lighting Control Circuit) It is shown in Figure 1.
Task number 1. More complicated. Create a diagram that allows you to turn on and off the light in your room with any of 3 different switches. Switches are located at the entrance to the room, above the bed and at the desk.
Task number 2.
In a sports committee, such as a factory committee, 5 judges gathered.
Each of them must vote for different decisions. The decision is adopted by a majority of votes, but only under the additional condition that the chairman of the committee vote for it.
The judges vote by pressing the button that closes the switch located under the table at which they are sitting. Closing the switch, they vote in favor, disconnecting the cons. Draw a simple diagram that allows you to automatically see the voting results. In the simplest case, simply with the help of a light bulb - lit up - the decision is made, did not light up - no.
Task number 3. In practice, this is unlikely, but as a complex educational task is quite suitable.
In a large hexagonal room, one switch is installed on each wall. Build a circuit so that at any time you can turn on or off the light in the room by turning one (any) switch.
After you unsuccessfully sit over tasks for three to four days, set them aside temporarily. And get busy Boolean algebra. It is Boolean algebra, or, as it is also called, Boolean algebra, relay circuit algebra, will help you to solve your problems.
What is Boolean algebra?
Oddly enough, despite the fact that for five years they have been studying algebra at school, many students, and later adults, will not be able to answer the question, what is algebra? Algebra is a science that studies the sets of some elements and the actions on them.
In a school course in algebra, such elements are numbers. Numbers can be denoted not by numbers, but by letters, everyone is familiar with this. In the first lessons of algebra, this always makes it difficult for many students. Remember how difficult it was at first to get used to folding letters instead of numbers, solving equations that didn't say anything.
Probably, each of us then asked ourselves the question: “Why do we need to enter letters instead of numbers and is it necessary at all?” And only later did you see what advantages algebra gives when solving problems in comparison with arithmetic.
Algebra is used in many exact sciences. This is physics, mechanics, sopromat, electricity. Ohm's law there is nothing more than an algebraic equation: it is enough to substitute their numerical values instead of letters to find out what current will flow in the load, or what resistance a section of the circuit has.
So you became acquainted with the algebra of numbers, or with elementary algebra. The main and almost unique task is to get an answer to the question: “What is X equal to? How many?"
In high school, they study the beginnings of vector algebra. This algebra is fundamentally different from elementary algebra. It has a different nature of the studied set and other rules of action. Solving the vector equation, we get in the answer a vector that is not an ordinary number that answers the question "How much?"
The formulas of vector algebra are in many respects different from the formulas of elementary algebra. For example, in elementary algebra and in vector algebra there is an addition operation. But it is performed in completely different ways.The addition of numbers is not at all the same as the addition of vectors.
There are other algebras: linear algebra, algebra of structures, algebra of rings, algebra of logic, or, what is the same, Boolean algebra. You probably didn’t hear the name in school lessons. George Boole - but everyone knows the name of one of his talented daughters Ethel Voinich (1864 - 1960). She wrote the novel "Gadfly", which talks about the struggle for the rights of Italian carbonarians.
 George Bull was born in England on November 2, 1815. All his life he worked as a teacher of mathematics and physics at school. From the memoirs of his students it is known what great importance Bul attached to the development of students' creative abilities. In presenting new material, he sought to ensure that his students themselves “rediscovered” certain formulas and laws.
George Bull was born in England on November 2, 1815. All his life he worked as a teacher of mathematics and physics at school. From the memoirs of his students it is known what great importance Bul attached to the development of students' creative abilities. In presenting new material, he sought to ensure that his students themselves “rediscovered” certain formulas and laws.
Telling students about the difficulties that scientists inevitably faced in the search for truth, the teacher liked to repeat one Eastern wisdom: even the Persian throne cannot bring so much pleasure to a person as the smallest scientific discovery. Buhl never lost hope that someday his students would make a real discovery.
The range of scientific interests of Buhl was very wide: he was equally interested in mathematics and logic - the science of laws and forms of thinking. In those days, logic was considered a humanities science, and many who knew George Boole were amazed at how the exact methods of cognition inherent in mathematics and purely descriptive methods of logic could coexist in one person.
But the scientist wanted to make the science of laws and forms of thinking as rigorous as any of the natural sciences, say mathematics and physics. For this, Boule began to denote not numbers as letters, as is done in ordinary algebra, but statements, and showed that such equations, very similar to algebraic ones, can solve questions about the truth and falsity of statements made by man. So the Boolean algebra arose.
But long before George Buhl, the German mathematician and philosopher Gottfried Leibniz (1646-1716) first expressed the idea of creating a science that would designate all the concepts of ordinary colloquial speech with symbols and establish some new algebra for combining these symbols.
After the creation of such a science, according to Leibniz, scientists and philosophers will stop arguing and shouting at each other, finding out the truth, but they will pick up a pencil and calmly say: “Let's calculate!”
 Today, the algebra of logic has become an important part of mathematics. One of its tasks is to solve all kinds of equations, the numerical ratios of which are replaced by alphabetic ones. Each of you, probably, throughout your life remembered how to solve equations of the second and third degree with letter coefficients. So, Boole in his new algebra used all these formulas and rules.
Today, the algebra of logic has become an important part of mathematics. One of its tasks is to solve all kinds of equations, the numerical ratios of which are replaced by alphabetic ones. Each of you, probably, throughout your life remembered how to solve equations of the second and third degree with letter coefficients. So, Boole in his new algebra used all these formulas and rules.
What is new in Boolean algebra is that the elements of the set that are studied in it are not numbers, but statements. If, when solving ordinary algebraic equations, it is determined what number equals unknown X, school algebra seeks the answer to the question: “How much?”
The algebra of logic is looking for the answer to the question: “Is this or that statement denoted by the letter X true?”
The meaning and content of the statement do not play any role here. Each statement can only be true or false. It cannot be half true and half false. As an example, we can recall tossing lots with a coin.
Only two coin states are considered there - heads or tails. By agreement of the parties, the eagle is YES, and tails are NO. No other intermediate points are taken into account in probability theory, although they are possible. A flipped coin can fall on an edge, roll down the floor to the legs of a chair or table and remain in an upright position, or even fall into a wide gap in the floor. (By analogy with electrical circuits, the last two situations can be considered as a malfunction in the form of a burnt contact).But in those days, Boolean algebra, alas, was not widely used.
 Claude Shannon “discovered” the Buhl algebra again. In 1938, while still a student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and America, young Claude proved that Boolean algebra is completely suitable for the analysis and synthesis of relay and switching circuits.
Claude Shannon “discovered” the Buhl algebra again. In 1938, while still a student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and America, young Claude proved that Boolean algebra is completely suitable for the analysis and synthesis of relay and switching circuits.
With the help of Boolean algebra, it is very easy to make an electrical circuit of an automaton operating on a relay.For this, it turns out, you only need to know exactly what the machine should do, that is, you need to have an algorithm for its operation. So the foundation was laid for the theory of digital machines operating on the principle of YES or NO.
Such, in brief, is the history of Boolean algebra. In the following articles we will consider its basic laws, examples of contact circuits implementing these laws. Consider the solution of those tasks that were given at the beginning of the article.
Continuation of the article: Boolean algebra. Part 2. Basic laws and functions
Boris Aladyshkin
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
: