Categories: Featured Articles » Home automation
Number of views: 5511
Comments on the article: 0
An example of using modern automation in a greenhouse
Greenhouses are constructions intended for growing natural vegetables in a shorter period of time than in open ground. The use of greenhouses is common both among private owners and in agriculture as a whole.
Previously, the automation of the greenhouse was an expensive and sometimes unbearable procedure, but at the moment the solution to this problem is not so expensive and quite pays off, and in the future, it will bring even greater benefits.

Many factors necessary for the effective cultivation of vegetable crops require the use of modern automation, for example:
1) Automatic maintenance of optimal air temperature;
2) Automatic watering;
3) Automatic inclusion of lighting;
4) Automatic soil heating.
Automatic maintenance of optimum air temperature
When growing tomatoes and cucumbers, as the most common crops grown in greenhouses, it is desirable that the air temperature be from +18 to +25 ° C during the day and not lower than +16 ° C at night. Soil temperature is from +10 ° С and higher.
Lowering the temperature is carried out using actuators that open the windows of the greenhouse for ventilation when the air temperature rises. For these purposes, you can also use stepper motors, upon a signal, open the vents to the desired angle.

Actuator
Actuators are preferably used not only with a temperature sensor, but also with a wind sensor, so as not to harm the plants. In the role of air temperature sensor, you can use a simple and inexpensive DS18B20 digital sensor.

SensorDS18B20
Watering plants
Automatic irrigation is carried out using moisture sensors that limit watering, but it is also better to use a water flow sensor together with them, since simple, inexpensive soil sensors oxidize very quickly and fail. For small farms, you can use homemade humidity sensors based on timer NE555.
This microcircuit cannot be called modern, but it has established itself as a reliable electronic tool used in many fields. The electrodes must be made of graphite, which is not oxidized. Output 3 of the microcircuit is connected to the LED, which signals the exit of humidity beyond. This output can also be connected to the control system and, upon a signal from it, can be disabled or turned on.
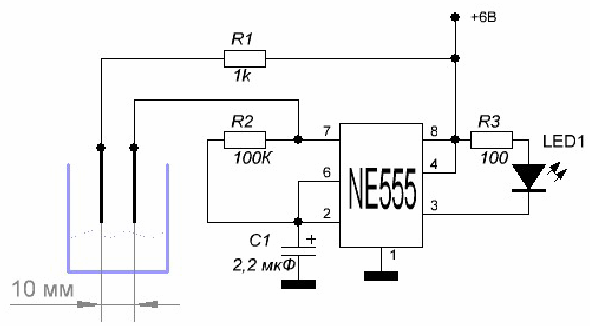
Soil moisture sensor on the NE555 chip
It is important to know the required water flow per day (which will depend on the area of the greenhouse, the needs of the plants grown in the water, their density, etc.), then it is sufficient to control the irrigation using water flow sensors over time, and use humidity sensors as overflow alarms.
Lighting control
Auto lighting is easiest to do with simple photoresistor. When the light decreases, its resistance increases and thus a control signal is formed to turn on the lights in the greenhouse.
Soil heating
Automatic soil heating is carried out just like air, but instead of actuators, temperature controls are used heating elements or heating cable.
Automation Control Devices
Separately, it should be said about devices that receive information from sensors, analyze and issue control signals to actuators, heating elements, water supply valves, etc. On the Internet you can find a lot of articles on such a platform as Arduino on the basis of which it is proposed to create automation of small greenhouses.
Arduino is a hardware-software tool with a bootloader previously flashed into it, which allows you to load your program into a microcontroller without using separate hardware programmers.The microcontroller on the board is programmed using the Arduino language, based on the Wiring language (C-like).
All the results of equipment operation in an automated greenhouse, if necessary, can be visually tracked on a computer.INeb interface can provide an opportunity not only to monitor the readings of temperature, humidity and lighting sensors, but also to control these very readings. It may also be possible to monitor the greenhouse through a webcam.
The greenhouse control system is controlled by a central board. Arduino, works as follows: the obtained environmental data, the humidity or lighting air temperature sensor is transmitted to the central controller (Arduino) which compares the current values with the given ones. If any of the values does not match, then the actuator is actuated to restore the optimal state. Further Arduino sends data to a remote server for monitoring via the Internet.
Arduino example for greenhouse automation
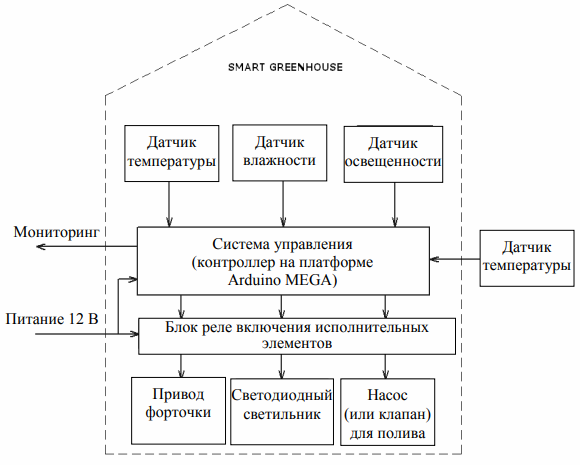
Arduino greenhouse automation circuit example
By means of a special programmable unit, control of such parameters as:
-
heating the interior of the greenhouse;
-
water heating;
-
frequency and duration of watering;
-
start and stop forced ventilation;
-
lighting.
Air temperature control is determined by two threshold limits: the upper limit and the lower limit. When the upper limit is exceeded, the air vents open, the fan is activated to cool the greenhouse environment, curtains can be used for oppression, and when the temperature drops below the lower limit, the fan turns off, the heater turns on to heat the air to a predetermined level.
Humidity control is determined by the threshold set by the user. when the humidity in the greenhouse drops below a predetermined threshold, the automatic irrigation system turns on and then turns off when the optimal state is restored.
The lighting condition is controlled by two given points: the upper limit and the lower limit. The upper limit determines when the light is activated while the lower limit determines when it is off. This strategy is mainly used to increase daylight or compensate for insufficient daylight according to the user's wishes.
Despite the simplicity of programming and connection, as well as the low cost, in my opinion, the implementation of such projects on the Arduino is difficult.
As a master control device can also be usedmicrocomputer Raspberry Pi 2combining the advantages of Arduino and a personal computer, as it is capable of launching a separate operating system and has input / output ports for connecting slaves and receiving signals from sensors.
But the easiest way is to buy a ready-made device in the form of a programmable relay or programmable logic controller. Of the domestic manufacturers of such products, OWEN, Segnetics, and others are best known. An alternative for those who have learned how to program Arduino can be the Controllino PLC.
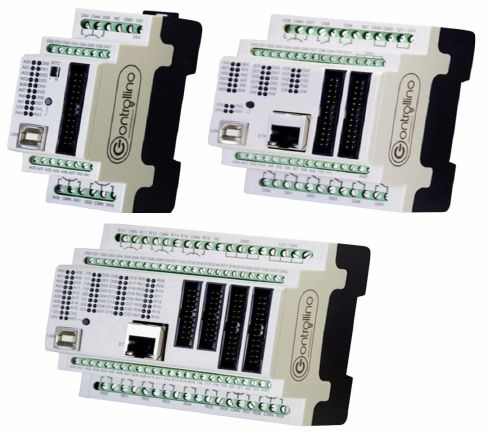

PLC Controllino: MINI (left), MAXI (middle) and MEGA (right)
The only disadvantage of this PLC is the relay outputs with a current of up to 6 A. But if the greenhouse uses electrical equipment with less current consumption, then this PLC is the best fit.
Today it is available in 3 versions: MINI, MEGA, MAXI. An important plus is the ability to connect to the Internet via the Ethernet interface for remote monitoring and control. This interface is available in MEGA and MAXI versions.
Thus, the creation of an automated greenhouse today is a simple and relatively inexpensive task for small farms.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
