Categories: Repair of household appliances
Number of views: 13,750
Comments on the article: 0
Types of fuses for household appliances
Those involved in the repair of equipment must have heard the joke: "The device burned out, protecting itself with a fuse." No matter how ridiculous it may sound, such situations happen quite often. Nevertheless, a fuse is an obligatory part of almost all types of household appliances. They are needed not only to protect the device itself, but also so that damage does not progress until fire. In this article we will tell you what fuses are used in household appliances.
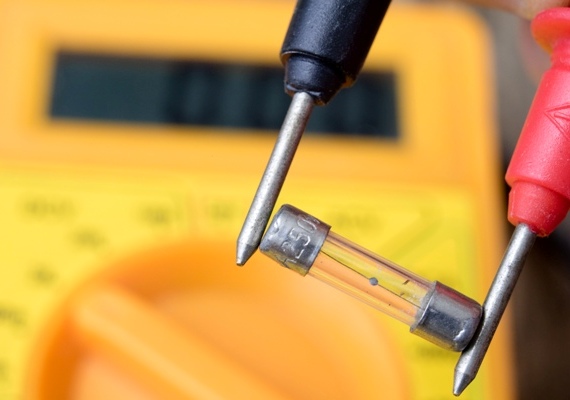

Definition
An electric fuse is a device or switching device designed to disconnect a circuit from a power source at a current significantly higher than the rated current. In simple words: if the device for some reason began to consume excessive current, the fuse will open the circuit. It is installed in series with the protected section of the circuit. In the diagram, the fuse is indicated as follows:
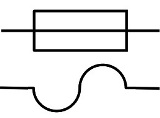
Kinds
Fuses are of different types by type of action:
-
Fusible;
-
Self-healing;
-
Thermal fuses;
-
Electromechanical.
-
Electronic.
Fuses or fuses are the most common, as their device is simple, as is their manufacture. They are used in most household appliances, cars. Previously used to protect apartment wiring - the so-called traffic jams.
Fuses - disposable. Thermal fuses designed to operate at a certain current within the permissible temperature. Also disposable, like fusible inserts.
Self-healing. As the name implies, these are reusable fuses. Used less frequently.
Electromechanical fuse sometimes called circuit breaker (automatic). It is used to protect wiring, electric motors, and other relatively powerful electrical appliances.
Electronic fuse - built on a measuring, control circuit and power transistoropening circuit when threshold current is reached. The most common device that works this way is the protection board. lithium battery.
In household appliances, you can find mainly fuses, as well as self-healing fuses, we will consider them in more detail.
Fuses
The easiest option is a fuse. It consists of a glass or ceramic case with a conductor inside. Depending on the current for which it is designed, it can be of different sizes, and also filled with quartz sand to extinguish arising arcs.
As the conductor, pure metals (not alloys) are chosen, such as: copper, zinc, iron, lead. Such metals are used as they have a positive thermal coefficient of resistance (TCR). That is, when heated, their resistance increases.
The shape of the fuses can be:
-
Tubular;
-
Fork (they are flag);
-
Cork;
-
Knife type.
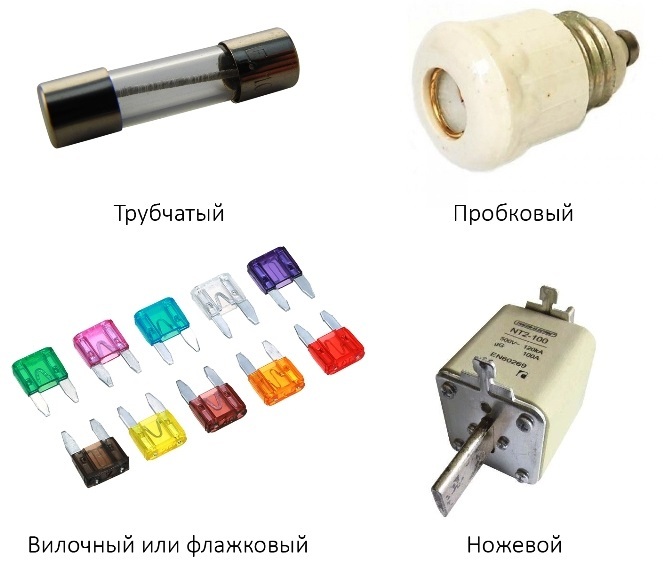

Note:
Fork or flag fuses are most often used in automotive wiring. Cork was used (found to this day) to protect apartment wiring and other circuits, installed, for example, on the meter. Knife fuses are used in power electrical cabinets (for example, nuclear reactors, nuclear reactors, ballasts).
Operating principle
When a current flows through a conductor, a certain power is released in it in the form of heat:
P = I2R
The same describes the Joule-Lenz law:
W = I2 * R * t
From the above it follows that the amount of heat generated depends on:
-
Current strength;
-
Conductor resistance
-
The time during which the current flowed.
Heat is dissipated in the environment, but when the conductor reaches a certain temperature, it begins to melt and burns out.This temperature is achieved in the case of a certain current flow. At the same time, due to a certain inertia of heating, the fuses do not burn out due to inrush currents and short-term overloads.
On practice
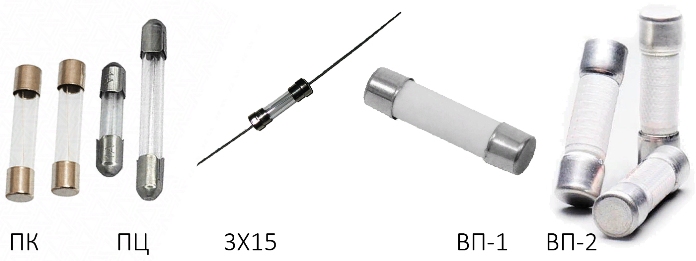
In household appliances, tubular fuses are used. They are usually designed for current up to 6A and come in different sizes (outer diameter x length):
-
3x15;
-
4x15 type VP-1;
-
5x20 type VP-2;
-
6x32 type, PC-30;
-
7x15;
-
10x30.
When a surge in the network, with short circuits in the circuit of the device fuse blows. With a positive development of the situation, the device remains intact. However, it often fails. What would happen if there were no fuses?
As a result of the breakdown diode bridge or transformer windings may cause a short circuit. The current consumption rises sharply. The wires and conductors begin to heat up. If none of this burns out, then the plug to which the device is connected to the network can be welded to the contacts of the outlet. The wiring will warm until it knocks out circuit breaker. However, such an outcome is possible that parts of the casing of a damaged device may ignite earlier. All this happens in a matter of moments.
It is in order to avoid such consequences after troubleshooting the device, and even if they were not there, and only the fuse is out of order - you need to replace it with a new one with the same or closest rated current. Please note that the design of the fuse must ensure the extinction of the arc that occurs when it blows out. This means that you can not put fuses intended for the car in devices that operate on a 220V network.
Although the fuses are worth a penny, but for the overall development you need to know how to repair them. To do this, remove the metal contact caps from the ends of the fuse and replace the wire. Usually it is soldered from the ends.

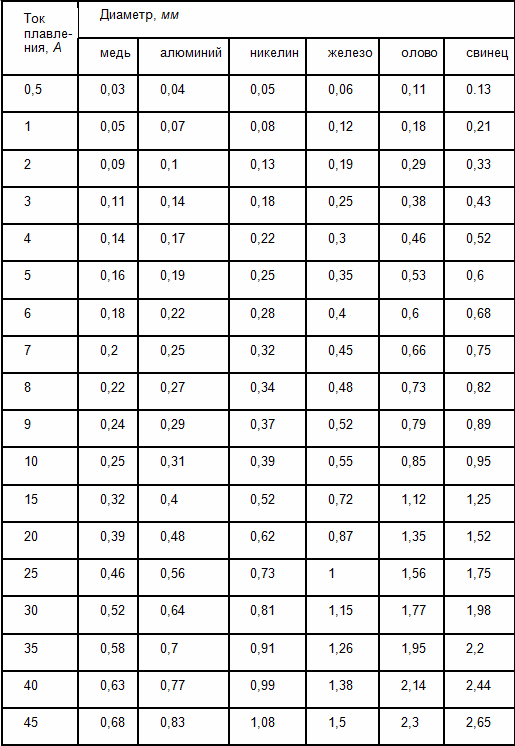
The new wire is selected as follows:
1. Determine the current consumed by the device.
I = P / U
2. According to the table, select the diameter of the wire according to the melting current. It is chosen 2 times more than the rated current consumption.
Thermal fuses
Thermal fuses are disposable protective elements, like fuses. They are used in circuits where not only protection against high current is needed, but also from overheating.
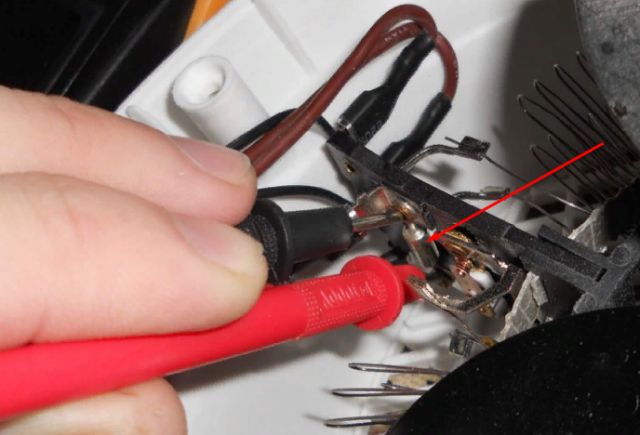

For example, they are used in modern household heaters. In the photo you see the thermal fuse in the fan heater. It will burn out if the permissible temperature is exceeded, for example, if the fan fails, so that the spirals do not overheat and a fire does not occur. They are also used in hair dryers, irons and more.
The main characteristics when choosing a fuse are its rated current and temperature, consider both of these factors when buying a replacement for a failed element.
It is worth noting that disposable thermal fuses are often installed to protect the windings of modern transformers. If it is located on top of the winding, you can replace it and the transformer will still serve, but if it is located in the depth of the winding, you won’t be able to replace it without rewinding skills.

But there are reusable thermal fuses. In them, under the influence of heat, the contact group switches. They come with normally closed (NC) and normally open (NO) contacts. The former, when heated, open the circuit, and the latter, on the contrary, close. After cooling, the contacts will return to their original position.
Therefore, when buying a new one in return for a failed one, pay attention to the type of contacts (NC or NO).

Resettable Fuses
This is a device with a positive temperature coefficient of resistance. With increasing current through its resistance increases nonlinearly.Resistance after tripping depends on two factors, namely, the applied voltage and power dissipation.
R = U2 / P
Below you see an example of a graph of resistance versus temperature.
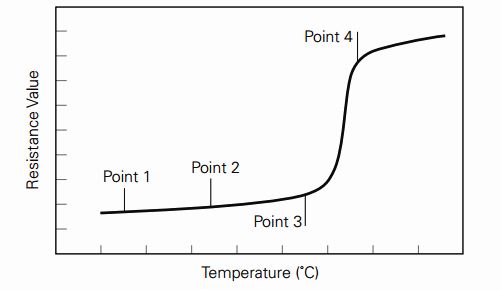
Along with an increase in resistance, the temperature of the device rises to the level of 80 degrees. They consist of a mixture of polymers and carbon.
They have the following specifications:
-
Vmax is the maximum allowable voltage.
-
Imax is the maximum current that can flow in a circuit without destroying a resettable fuse.
-
Ihold - rated current.
-
Itrip - the minimum current that can flow through the device without causing it to trip.

Resettable fuses are often used to protect digital electronics, such as protecting USB, HDMI, less commonly in portable power circuits with batteries.
Conclusion
We examined the main types of fuses that are found in household appliances. This is an important part on which the safe operation of the device depends. Do not use “bugs” - wire windings in the event of a fuse failure and do not remove them from the circuit by shunting for permanent operation.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
