Categories: Featured Articles » Novice electricians
Number of views: 5238
Comments on the article: 0
The most popular electrical insulation materials
The modern electrochemical industry boasts a wide variety of electrical insulating materials. Glass fiber materials, which include synthetic resins, deserve special attention, since these materials are not only highly electric, but also have significant mechanical strength, as well as heat and moisture resistance.

Natural electrical insulating materials, such as mica and asbestos, artificial counterparts - electric cardboard and cotton tapes - share the market for modern electrical insulation with high-quality fiberglass, which is part of fiberglass fabrics, fiberglass, fiberglass and fiberglass. In addition, synthetic films are widely used: melinex, lavsan and others.

It is thanks to the appearance of synthetics in the composition of insulating materials that the power and durability of modern electrical and electronic equipment have greatly increased, and the dimensions (transformers, reactors, capacitors, motors and many other electrical units) have remained the same. Let's look at the most popular of electrical insulating materials of our time.
Electric board
Electrocardboard of the EV and EVT brands from 0.1 to 0.3 mm thick is intended for operation in the air. To work in oil, EMC and EMT electrocardboard with a thickness of 1 to 3 mm are used.
Electrocardboard is available in the form of sheets or rolls. An impregnated electrical board is vulnerable to moisture, so it requires dry storage. Nevertheless, even at a moisture content of 8%, EV grade cardboard has a dielectric strength of the order of 10 kV / mm, while for the EMT grade the characteristic dielectric strength under normal conditions reaches 30 kV / mm.
Electrical paper

Made from softwood treated with alkali, insulating paper, depending on the thickness and composition, is divided into several types: telephone, cable and capacitor. KT-05 brand paper has a thickness of about 0.05 mm. The cable paper K-120 is characterized by a thickness of 0.12 mm, it is additionally impregnated with transformer oil, which gives high dielectric characteristics.
Condenser paper is also impregnated with transformer oil, but its thickness is much less than in the two previous types.
Fiber

The starting material for fiber is paper, which is treated with a solution of zinc chloride. And although the fiber is mechanically weak, vulnerable to acids and alkalis, nevertheless it is easy to process, and the dielectric strength of the fiber reaches 11 kV / mm.
Fiber is produced in the form of rods, tubes or sheets with a thickness of 0.6 to 12 mm. Fiber is used in the manufacture of electrical gaskets and coil frames. A type of thin fiber (thickness from 0.1 to 0.5 mm) is a leteroid, which can be found on sale in the form of sheets or rolls.
Kiper tape

As the first representative of the family of cotton tapes, we consider the keeper tape of LE. It is made from cotton thread, produced in a thickness of 0.45 mm and a width of 10 to 60 mm. Kiper tape is used to tighten wires and cables, for tying the windings of transformers and motors, also kiper tape is used for tying various coils and other electrical work.
Tufted tape

Silk or cotton thread is used in the manufacture of taffeta tapes LE. Tufted tape can be from 10 to 50 mm wide. The thickness of the tufted tape is traditionally 0.25 mm, which is less than that of the keeper tape, and therefore it is inferior in strength to it. Tufted tape is also used in electrical work.
Batiste tape

A thinner alternative to taffeta tape is the LE cambric tape, made from cotton weaving. It can have a width of 10 to 20 mm, and a thickness of 0.12 to 0.18 mm.
Calico tape

Less durable than kiper tape, but stronger than tufted tape - 0.22 mm thick - calico. Available in widths from 12 to 35 mm.
Asbestos
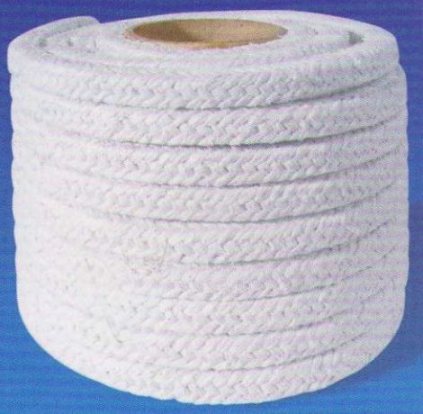

The fibrous natural mineral Asbest is characterized by high heat resistance and low thermal conductivity. It is capable of demonstrating dielectric properties acceptable for some applications at operating temperatures up to 400 ° C.
The characteristic dielectric strength of asbestos barely reaches 1.2 kV / mm, therefore, they resort to its use precisely because of its high heat resistance, using it as a heat insulator. If asbestos is used for electrical insulation, then only in low-voltage electrical installations. Asbestos is traditionally produced in the form of sheets or ropes.
Varnish and fiberglass
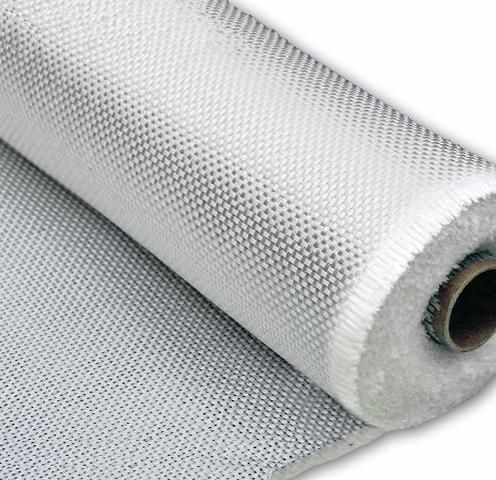

Silk, glass or cotton threads are used for the production of flexible fiberglass and varnished fabrics of various grades, produced in the form of rolls with a material thickness of 0.1 to 0.3 mm and a width of 700 to 1000 mm. The fabric is impregnated with oil or oil-bitumen varnish or other suitable electrical insulating composition.
The LSHSS silk lacquer fabric can be very thin - up to 0.04 mm. LSC fiberglass is characterized by heat resistance up to 180 ° С, and electric strength reaches 40 kV / mm. Fiberglass and varnish are traditionally used for interlayer insulation of coils.
Thin film materials

Ftoroplastovaya, polyethylene terephthalate and dacron films, as well as film electrocardboard (electrocardboard glued with a thin film) are characterized by high electrical strength - up to 200 kV / mm and significant mechanical strength - with a film thickness of 0.05 mm, tensile strength reaches 30 kg. The heat resistance of these films is above 120 ° C.
Textolite, fiberglass, getinaks

The first representative of laminated electrical insulation materials is textolite. It is produced by pressing multilayer cotton fabric impregnated with a resol resin. Pressing is carried out at a temperature of 150 ° C. The resulting material is characterized by very high mechanical strength, however, it is less moisture resistant than getinaks.
On the market, textolite is presented in the form of tubes, cylinders and sheets. Due to the fact that textolite can be easily machined, coil frames, dielectric gaskets and shields, printed circuit boards and even gears and bearing shells are made from it.

Unlike textolite, fiberglass fabric is not used in the production of fiberglass, but fiberglass. For this reason, the electric strength of fiberglass is up to 20 kV / mm, which is higher than that of getinaks and ordinary textolite. Moisture resistance is also better than PCB and higher heat resistance - reaches 225 ° C. The market value of fiberglass is higher than that of textolite.

The simplest representative of laminated electrical insulation materials is getinax. In fact - compressed paper impregnated with bakelite resin. Getinax is produced in the form of sheets from 0.4 to 50 mm thick, as well as in the form of rods of various diameters. Its electric strength reaches 25 kV / mm. It is used for the same purposes as textolite, however, taking into account the fact that the heat resistance of getinaks is lower, and with excessive heating it is carbonized and becomes a conductor.
Mica
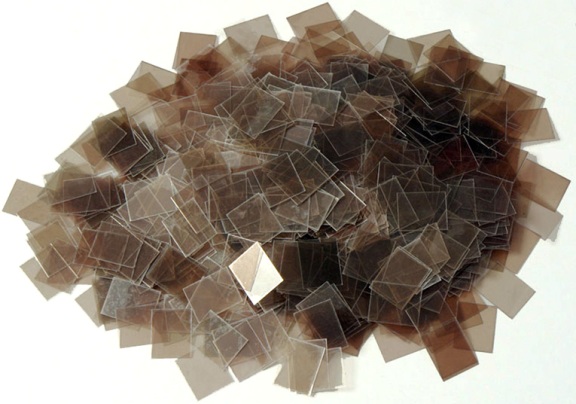

The crystalline natural mineral, mica, serves as an excellent raw material for creating high-quality insulating materials. The layers of the mineral are glued together with resin or varnish to obtain muscovite or micanite. Muscovite is used in capacitors, as it has the best characteristics.
Mikanit - used for the production of dielectric gaskets and windings of electrical machines.Heat resistance of mica materials reaches 180 ° C, dielectric strength - up to 20 kV / mm. In addition, it is worth noting the excellent moisture resistance of mica. By gluing mica onto the fabric, a mikalent is obtained with a thickness of 0.08 to 0.17 mm and a width of 12 to 35 mm.
Nowadays, mica is in short supply, so even mica waste goes into business - mica paper, glass mica, etc., which are also used as electrical insulating materials with dielectric characteristics close to mica, are made from waste.
Porcelain and steatite

Electrical ceramics occupies a special place among electrical insulating materials. Its main types are porcelain and steatite. Electrical porcelain is characterized by dielectric strength up to 28 kV / mm and heat resistance up to 170 ° C. Its high strength and moisture resistance make porcelain an ideal material for the manufacture of insulators. Porcelain is widely used in electrical engineering, electronics, automation and IT-sphere.
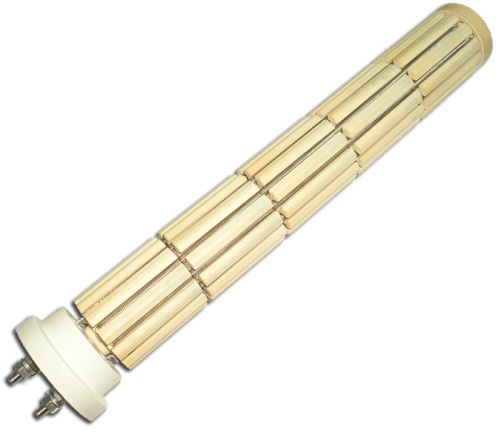

Steatite surpasses porcelain in dielectric strength (up to 50 kV / mm). That is why steatite is used for the manufacture of particularly important electrical components where heat resistance and particularly reliable electrical insulation are required. High-quality heating elements are coated with steatite precisely because of its high heat resistance.
See also:Examples of the use of ceramic materials in electrical engineering and electric power industry
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
