Categories: Featured Articles » Novice electricians
Number of views: 13405
Comments on the article: 0
DC voltage regulation
Today, both in industry and in the civilian sphere, there are many installations, electric drives, technologies, where power supply requires not alternating, but constant voltage. Such installations include various industrial machines, construction equipment, electric transport engines (metro, trolleybus, forklift, electric car), and other DC installations of various kinds.
The supply voltage for some of these devices must be variable so that, for example, a varying current supply to the electric motor leads to a corresponding change in the rotational speed of its rotor.
One of the first ways to regulate DC voltage is to regulate with a rheostat. Then we can recall the circuit engine - generator - engine, where again by adjusting the current in the excitation winding of the generator, a change in the operating parameters of the final engine was achieved.
But these systems are not economical, they are considered obsolete, and regulatory schemes are much more modern. based on thyristors. Thyristor regulation is more economical, more flexible, and does not lead to an increase in the overall mass-dimensional parameters of the installation. However, first things first.
Rheostatic regulation (regulation with additional resistors)
Regulation by means of a chain of series-connected resistors allows you to change the current and voltage of the electric motor by limiting the current in its anchor circuit. Schematically, it looks like a chain of additional resistors connected in series to the motor winding, and connected between it and the positive terminal of the power source.
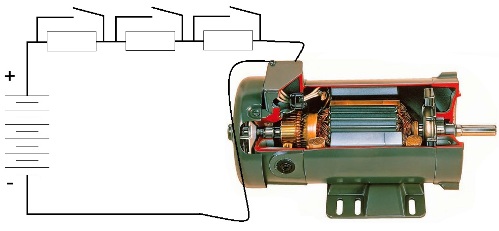
Some resistors can be shunted by contactors as needed so that the current through the motor winding changes accordingly. Previously, in traction electric drives, this method of regulation was very widespread, and for the lack of alternatives, it was necessary to put up with very low efficiency due to significant heat losses on the resistors. Obviously, this is the least effective method - excess power is simply dissipated in the form of unnecessary heat.
Regulation on the engine - generator - engine system
Here, the voltage to power the DC motor is obtained locally using a DC generator. The drive motor rotates the DC generator, which in turn feeds the actuator motor.
The regulation of the operating parameters of the actuator motor is achieved by changing the current of the excitation winding of the generator. The current of the generator field winding is higher - the higher voltage is supplied to the final motor, the lower the field current of the generator field - lower voltage, respectively, is supplied to the final motor.
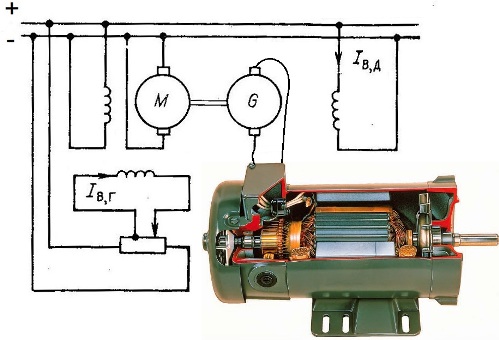
This system, at first glance, is more efficient than simply dissipating energy in the form of heat through resistors, but it also has its drawbacks. Firstly, the system contains two additional, fairly large-sized, electric machines that need to be serviced from time to time. Secondly, the system is inertial - the connected three machines are not able to sharply change their course. As a result, again the efficiency is low. However, for some time, such systems were used in factories in the 20th century.
Thyristor control method
With the advent of semiconductor devices in the second half of the 20th century, it became possible to create small-sized thyristor regulators for DC motors.The DC motor was now simply connected to the AC mains through the thyristor, and by varying the opening phase of the thyristor, it became possible to obtain smooth control of the rotor speed of the motor rotor. This method allowed to make a breakthrough in raising the efficiency and speed of converters for powering DC motors.
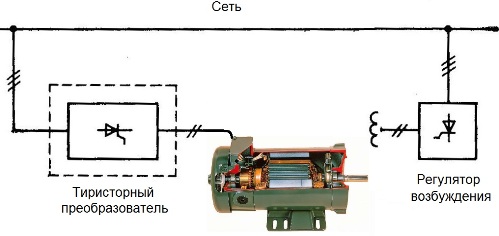
The thyristor control method is now also used, in particular, to control the rotation speed of the drum in automatic washing machines, where a collector high-speed motor serves as a drive. In fairness, we note that a similar regulation method works in thyristor dimmers, which can control the brightness of the glow of incandescent lamps.
PWM-based control with AC link
The direct current is converted by an inverter into alternating current, which is then increased or decreased by a transformer, and then rectified. The rectified voltage is applied to the windings of the DC motor. Perhaps additional pulse regulation by PWM modulation, then the achieved output effect is somewhat similar to thyristor regulation.
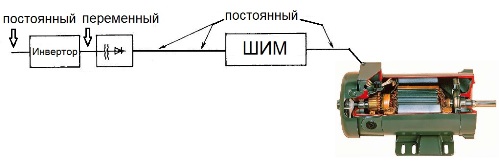
The presence of a transformer and an inverter, in principle, leads to a rise in the cost of the system as a whole, however, the modern semiconductor base allows you to build converters in the form of finished small-sized devices powered by AC mains, where the transformer costs a high-frequency pulse, and as a result the dimensions are small, and the efficiency already reaches 90 %
Impulse control
The impulse control system of DC motors is similar in its design to a pulse DC-DC converter. This method is one of the most modern, and it is used today in electric cars and implemented in the subway. The link of the step-down converter (diode and inductor) is combined in a serial circuit with the motor winding, and by adjusting the width of the pulses supplied to the link, they achieve the required average current through the motor winding.
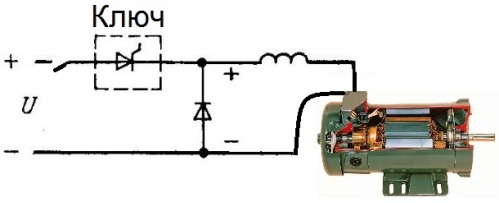
Such pulse control systems, in fact - pulse converters, are characterized by higher efficiency - more than 90%, and have excellent speed. It offers great opportunities for energy recovery, which is very important for machines with high inertia and for electric cars.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
