Schmitt trigger - general view
 During the design of the pulse circuit, the developer may need a threshold device that could form a pure rectangular signal with certain values of high and low voltage levels from the input signal of a non-rectangular shape (for example, sawtooth or sinusoidal). The Schmitt trigger, a circuit with a pair of stable output states, which under the influence of the input signal, replace each other in a jump, is well suited for this role, that is, the output is a rectangular signal.
During the design of the pulse circuit, the developer may need a threshold device that could form a pure rectangular signal with certain values of high and low voltage levels from the input signal of a non-rectangular shape (for example, sawtooth or sinusoidal). The Schmitt trigger, a circuit with a pair of stable output states, which under the influence of the input signal, replace each other in a jump, is well suited for this role, that is, the output is a rectangular signal.
A characteristic feature of the Schmitt trigger is the presence of a certain range between the voltage levels for the input signal, when the output voltage of the input signal is switched over at the output of this trigger from a low level to a high one and vice versa. This property of a Schmitt trigger is called hysteresis, and the portion of the characteristic between the threshold input values ...
Discrete Component Field Effect Transistor Driver
 It’s one thing when there is a ready-made driver in the form of a specialized microcircuit like UCC37322 for high-speed control of a powerful field-effect transistor with a heavy gate, and it’s quite another when there is no such driver, and the power switch control scheme must be implemented here and now.
It’s one thing when there is a ready-made driver in the form of a specialized microcircuit like UCC37322 for high-speed control of a powerful field-effect transistor with a heavy gate, and it’s quite another when there is no such driver, and the power switch control scheme must be implemented here and now.
In such cases, it is often necessary to resort to the help of discrete electronic components that are available, and already from them to assemble the shutter driver. The case, it would seem, is not tricky, however, in order to obtain adequate time parameters for switching the field-effect transistor, everything must be done efficiently and work correctly. A very worthwhile, concise and high-quality idea with the goal of solving a similar problem was proposed back in 2009 by Sergey BSVi in his blog. The circuit was successfully tested by the author in the half-bridge at frequencies up to 300 kHz. In particular, at a frequency of 200 kHz, with a load capacitanceat 10 nF ...
Choosing a driver for MOSFET (example calculation by parameters)
 FET gate control is an important aspect in the development of any modern electronic device. For example, when only the bottom is used in a pulse converter power key, and the decision was made in favor of using an individual driver in the form of a specialized microcircuit, it is necessary to solve the problem of selecting a suitable driver so that it can satisfy the following conditions.
FET gate control is an important aspect in the development of any modern electronic device. For example, when only the bottom is used in a pulse converter power key, and the decision was made in favor of using an individual driver in the form of a specialized microcircuit, it is necessary to solve the problem of selecting a suitable driver so that it can satisfy the following conditions.
First, the driver will need to provide reliable opening and closing of the selected key. Secondly, it is necessary to comply with the requirements for an adequate duration of the leading and trailing edges during switching. Thirdly, the driver itself should not be overloaded while working in the circuit. At this stage, it is advisable to start by analyzing the data from the documentation for the field-effect transistor, and from them, determine what the characteristics of the driver should be ...
RCD snubber - principle of operation and calculation example
 During the development of a power pulse converter (especially for powerful push-pull and forward topology devices, where switching occurs in hard modes), care must be taken to protect the power switches from voltage breakdown.
During the development of a power pulse converter (especially for powerful push-pull and forward topology devices, where switching occurs in hard modes), care must be taken to protect the power switches from voltage breakdown.
Despite the fact that the fieldwork documentation indicates the maximum voltage between the drain and source at 450, 600 or even 1200 volts, one random high-voltage pulse on the drain may be enough to break the expensive (even high-voltage) key. Moreover, neighboring elements of the circuit, including a scarce driver, may come under attack.Such an event will immediately lead to a bunch of problems: where to get a similar transistor? Is it on sale now? If not, when will it appear? How good will the new fieldwork be? Who, when and for what money will undertake to solder all this? ...
Inch * degree / watt - what is this radiator parameter?
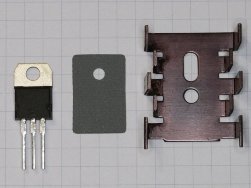 When approaching the question of choosing a radiator for a power transistor or a powerful diode, as a rule, we already have the result of preliminary calculations regarding the power that the component will need to dissipate through the radiator against the surrounding air. In one case, it will be 5 watts, in the other 20, etc.
When approaching the question of choosing a radiator for a power transistor or a powerful diode, as a rule, we already have the result of preliminary calculations regarding the power that the component will need to dissipate through the radiator against the surrounding air. In one case, it will be 5 watts, in the other 20, etc.
To dissipate more power, you need a radiator with a larger surface contact area with air, and if for the same transistor operating in the same mode, take a smaller radiator, then the radiator will be more heated. Thus, the statement is true for the same key: the larger the surface area of the radiator in contact with air, the more heat will be dissipated, and the less the radiator will heat up. That is, the longer the radiator and the more branched its profile is, the better it will dissipate heat and, accordingly ...
Methods and circuits for controlling a thyristor or triac
 Thyristors are widely used in semiconductor devices and converters. Various power sources, frequency converters, regulators, excitation devices for synchronous motors and many other devices were built on thyristors, and recently they are being replaced by transistor converters. The main task for the thyristor is to turn on the load at the time the control signal is applied. In this article we will look at how to control thyristors and triacs.
Thyristors are widely used in semiconductor devices and converters. Various power sources, frequency converters, regulators, excitation devices for synchronous motors and many other devices were built on thyristors, and recently they are being replaced by transistor converters. The main task for the thyristor is to turn on the load at the time the control signal is applied. In this article we will look at how to control thyristors and triacs.
Thyristor (trinistor) is a semiconductor semi-controlled key. Semi-controlled - means that you can only turn on the thyristor, it turns off only when the current in the circuit is interrupted or if a reverse voltage is applied to it. He, like a diode, conducts current in only one direction. That is, for inclusion in the AC circuit to control two half-waves, two thyristors are needed, for each one, although not always. The thyristor consists of 4 semiconductor regions (p-n-p-n) ...
How to use photoresistors, photodiodes and phototransistors
 Sensors are completely different. They differ in principle of action, the logic of their work and the physical phenomena and quantities to which they are able to respond. Light sensors are not only used in automatic lighting control equipment, they are used in a huge number of devices, from power supplies to alarms and security systems.
Sensors are completely different. They differ in principle of action, the logic of their work and the physical phenomena and quantities to which they are able to respond. Light sensors are not only used in automatic lighting control equipment, they are used in a huge number of devices, from power supplies to alarms and security systems.
A photodetector in a general sense is an electronic device that responds to a change in the light flux incident on its sensitive part. They may differ, both in structure and in principle of operation. Let's look at them. A photoresistor is a photographic device that changes the conductivity (resistance) depending on the amount of light incident on its surface. The more intense the illumination of a sensitive area, the less resistance. It consists of two metal electrodes, between which there is ...
What is a PWM controller, how is it arranged and works, types and schemes
 Previously, a circuit with a step-down (or step-up, or multi-winding) transformer, a diode bridge, a filter to smooth out ripples was used to power the devices. For stabilization, linear circuits were used on parametric or integrated stabilizers. The main drawback was the low efficiency and high weight and dimensions of powerful power supplies.
Previously, a circuit with a step-down (or step-up, or multi-winding) transformer, a diode bridge, a filter to smooth out ripples was used to power the devices. For stabilization, linear circuits were used on parametric or integrated stabilizers. The main drawback was the low efficiency and high weight and dimensions of powerful power supplies.
All modern household electrical appliances use switching power supplies (UPS, UPS - the same thing).Most of these power supplies use a PWM controller as the main control element. In this article we will consider its structure and purpose. A PWM controller is a device that contains a number of circuitry solutions for managing power keys. At the same time, control is based on information obtained through feedback circuits for current or voltage ...
