Categories: Sources of light, All about LEDs
Number of views: 55819
Comments on the article: 1
Parameters of LED light sources, characteristics of LED lamps
 Given the high popularity led light sources both among buyers and sellers, it is necessary to dwell in more detail on what parameters are used to characterize the consumer properties of such lamps, which, in fact, should be paid attention to when buying.
Given the high popularity led light sources both among buyers and sellers, it is necessary to dwell in more detail on what parameters are used to characterize the consumer properties of such lamps, which, in fact, should be paid attention to when buying.
1. First of all, any lamp, including LED, is characterized power consumption (watt). Typically, the power of LED lamps for domestic purposes ranges from 1 to 10 watts, although there are much more powerful sources for street lighting - 100 watts or more. Strictly speaking, the power consumption characterizes only the rate of energy consumption from the network, and in order to understand how much the lamp shines, you should ask the seller about the amount of light output.
2. Light flow measured in lumens and most fully characterizes the light source in terms of its ability to illuminate the room. Unfortunately, very often data on the luminous flux of LED lamps sold are simply not available, but instead some power is indicated on the package incandescent lamps, which gives the same luminous flux.
This data is pretty crafty, because it cannot be verified correctly. For example, on the packaging of an LED lamp it is written finely: the luminous flux is 280 lm, or there is no data on the flow at all, and a large image shows: 4 W power is equivalent to a 50 W lamp, and it is difficult to argue here, maybe there is some kind of incandescent lamp which consuming 50 watts will give only 280 lm. Only a normal incandescent lamp with a power of 50 W should give about 560 lm.
However, the question of equivalent power important for the buyer, especially if he selects LED lamps instead of the existing incandescent lamps. It is more correct to proceed from the data on the luminous flux of LED lamps, recounting them to the equivalent power of incandescent lamps. Here you can focus on the parameters of lamps from a well-known manufacturer, for example OSRAM.
The data from the 2012 catalog are shown in the table:
Luminous flux of lamps OSRAM series CLASSIC A (pear)
Even more difficult is the situation when it is necessary to determine the equivalent power when replacing halogen lamps. If the halogen lamp is 220 V, then you can focus on the above table, but if you choose a replacement for a 12 volt lamp, then we must remember that the light flux for these lamps is much higher at the same power, so you need to make a correction. The correction factor depends on the type of halogen lamp and can be determined using the table:
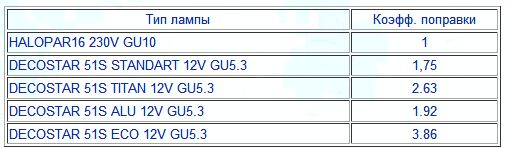
For example, let the LED lamp have a luminous flux of 240 lm and you need to replace the old 60 W incandescent lamps. According to the first table, such an incandescent lamp has a light output of 710/60 = 11.8 lm / W. Thus, the power of an incandescent lamp equivalent power led lamp It turns out 240 / 11.8 = 20 watts. Thus, to replace a chandelier of three sixty-watt lamps, 9 such LED bulbs are needed. I draw your attention to the conditional example, there are much more powerful LED lamps, which will require significantly less.
If you need to find a replacement for a TITAN halogen lamp, then in accordance with the second table the equivalent power will be 20 W / 2.63 = 7.6 W. Thus, in order to replace one TITAN 35 W lamp, 4-5 such LED lamps are required.
3. In addition to the total amount of luminous flux, how this luminous flux is distributed in space matters. The direction of the light distribution is characterized by the angle of divergence of the lamp. This parameter is set for light sources that produce directional radiation. A divergence of 120 ° means that the luminous intensity decreases by 2 times in the direction of the angle of 60 ° with the axis of the light beam of the lamp. Lamps with a divergence of 120 ° have a very wide radiation pattern, almost like a uniformly bright platform.
The wide angle of the lamp radiation favorably affects the uniformity of lighting in the room, but there is one subtlety here, which is that LED lamps have high brightness at large angles to the emitting plane, which can be uncomfortable. In this regard, attention should be paid to meeting the requirements for the presence of a protective angle when installing wide-angle LED lamps in luminaires, including in mortise ceiling. Lamps with narrow radiation (20-30 °) are used for accent lighting, but are not suitable for general.
4. Colour temperature - a parameter that determines the shade of the color of the radiation of the lamp. Warm white light corresponds to a color temperature of 2700 - 3500 ° K (2700 - has a noticeable yellow hue, provides a cozy, not too strong lighting, 3500 - whiter and stronger). Color temperature 4000 - 5000 ° corresponds to a neutral white light, provides a strong and comfortable lighting. 6500 ° and above - cold-white light for an amateur, often used for street lighting (since at this color temperature higher light output is realized).
5. Another important parameter color rendering coefficient, which characterizes the correct perception of the color of objects when illuminated by a lamp. The color rendering coefficient should be indicated on the lamp packaging and for LED sources intended for indoor lighting, cannot be less than 70 (for outdoor lighting - 60).
6. Maybe the most important thing for LED lamps - life time. Usually indicate very large numbers: 50,000, 30,000 hours. However, everything here is far from simple. In accordance with the "Law on the Protection of Consumer Rights", the service life is the period during which you can make a complaint to the manufacturer if his fault is established that the product is out of order.
An LED lamp can shine for a very long time, but over time, the amount of emitted light decreases noticeably, the light flux degrades, and the process speed depends on the heating temperature of the emitting crystal. Therefore, when evaluating LED lamps, it is more correct to talk about the period during which the light flux degrades no more than a given value. In accordance with applicable standards, a decrease in luminous flux of not more than 30% within 25,000 hours is considered acceptable.
7. Ripple factor - an important parameter characterizing the presence of rapid changes in light flux, invisible to the eye, but adversely affect fatigue. The requirements for the ripple coefficient are established in SP 52.13330.2011.
Unfortunately, data on the value of the ripple coefficient, as a rule, are not indicated on the package of lamps. It is hoped that during certification tests the compliance of this parameter with the requirements was checked. From general considerations, we can assume that LED strips and lightsthat are powered by separate stabilized sources of constant voltage or current, ripple is minimal. For lamps with primitive power supplies built into the base, the ripple can be much greater.
In addition to the above, requirements for LED light sources are also required for other parameters: power factor, energy efficiency (light output), etc.
See also on our website:
Main types and marking of LED lamps
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
