Categories: Featured Articles » Sources of light
Number of views: 3184
Comments on the article: 0
What is LED degradation?
Most often, speaking about the degradation of the LED, they mean the process of a gradual decrease in its brightness due to poor cooling of the crystal. Under the concept of “degradation of the LED” can also be meant the premature arrival of a semiconductor light source inappropriateness or a change in the original color temperature.
However, degradation can be caused by various reasons, despite the fact that the result always looks the same - an unacceptable decrease in the brightness of the LED or in general the cessation of light emission in response to a power supply.
LED degradation can be a real problem where color accuracy is crucial, such as in hospitals, exhibition halls, and museums. Let's look at the causes of LED degradation.
So, as we have already found out, the aging process of an LED is called degradation. First of all, this is expressed in a decrease in the brightness of the emitted light (in a decrease in luminous flux).
In addition, the problem becomes the so-called color shift, which is expressed in the deviation of the color temperature from the originally declared, and in the deterioration of color reproduction. Finally, everything can end with a complete failure of the LED. But anyway, various factors can lead to degradation of the LED.
One of the most common causes of early crystal degradation is poor assembly. Wanting to make the product as cheap as possible, to reduce its cost as much as possible, the manufacturer strongly deviates from adequate production standards, for example, using obviously small cases.
Modern models of high-power LEDs require new cases with a larger area than those cases that were previously used for low-power chips.
Or, the chips themselves can be made poorly, in violation of the correct technology. This unambiguously causes early crystal degradation, the LED will fail before the warranty period declared by the arrogant manufacturer.
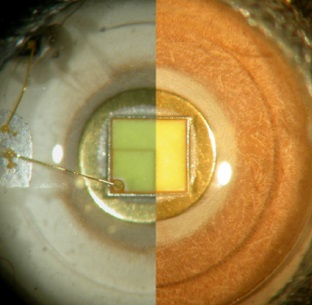
Due to poor installation, the LED crystal falls into the wrong operating conditions. It happens that an aluminum profile is not used at all when it should - this is a gross violation of the installation rules.
Installing a powerful modern LED on a chip that was used in low-power LEDs of earlier models leads to a guaranteed overheating of the crystal.
Mechanical damage - also lead to early degradation of the LED. Placing LEDs in direct sunlight or overheating during soldering by an inexperienced beginner is all a violation of the operating conditions of semiconductor light sources.
The listed factors have one thing in common - they contribute to poor heat removal from the crystal, lead to its overheating, which does not correspond to safe operating conditions.
The current through the junction can be exceeded due to one of these factors, and the diode will simply burn out, as well as in case of accidental overheating with a soldering iron. Exceeding the permissible temperature inside the device is the right way to rapid degradation of the crystal.

But even if the LED is operated correctly, then after a certain time the degradation of the crystal can still not be avoided. The fact is that LEDs themselves are subject to natural aging. White LEDs age especially quickly. The color of the white LED initially has a blue tint, which is usually aligned to white using a suitable phosphor.
The phosphor tends to coagulate over time, its layer eventually collapses, and the color temperature creeps in the direction of cold blue.
With another method of manufacturing LEDs, degradation occurs with a color shift towards yellow, since high temperatures cause air gaps between the luminescent coating and the LED chip, simply “delamination” of the LED occurs.
Both that and another - natural degradation, the nature of which the conscientious manufacturer always calculates at the manufacturing stage and takes into account when drawing up the specification for the LED.
It must be remembered that the specification of the LED manufactured at the plant, including the durability indicators, is compiled in laboratory conditions, where the perfectly correct modes of power, heat removal and humidity are observed. When operating in real conditions, durability is usually reduced.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
