Categories: Sources of light, Energy saving
Number of views: 18172
Comments on the article: 1
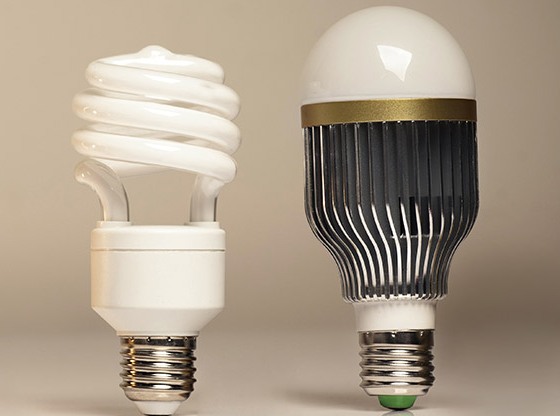
The difference between LED lamps and energy-saving compact fluorescent
Household consumers are gradually phasing out incandescent lamps, and they are using them less and less. At first they were replaced by compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs). They consume 5 times less energy at the same brightness. That is, a 20 W fluorescent lamp can replace a 100 W incandescent lamp. For this they were called energy-saving.
Technology does not stand still and in the last 5 years the market has strengthened LED bulbs or LED. The range of products is wide enough from light panels and tapes to searchlights and lamps for all possible socles. At the same time they shine 10 times brighter than incandescent lamps of the same power. Let's take a closer look at the differences between energy-saving and LED lamps.

Interesting:
LED lamps actually also belong to energy-saving ones, but in the people this name is fixed to compact fluorescent lamps, although they save energy not like LED ones. In the article, I propose not to deviate from popular names.
Composition
Energy savers are a compact version of the classic tubular fluorescent lamp, which are available under pin caps g5 and g13, usually differ in tube thickness (t5, t8). Compactness is achieved by twisting the tube in a spiral shape. Then, with the same principle of operation, you get a light source in size and base repeating common incandescent lamps.
The most popular models of lamps with socles E14 and E27.
The compact energy-saving lamp consists of:
-
basement;
-
housing;
-
electronic ballast;
-
flasks.
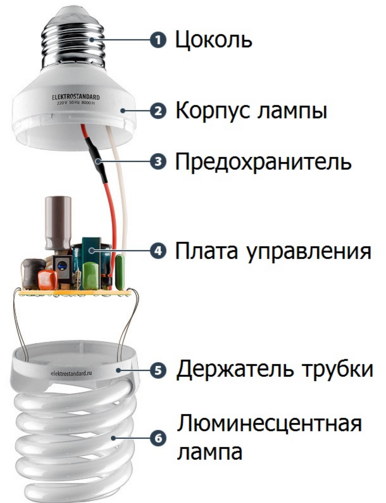
In turn, the flask is filled with mercury vapor and its inner walls are covered with a phosphor, the color spectrum and color temperature depend on its composition.
LED lamps, depending on the years of production, were built using various design and circuit solutions, types of LEDs. Early models were produced with 5 mm LEDs, later they were replaced SMD LEDssuch as you might come across on an LED strip.
The latest innovations are filament filaments, they consist of LED crystals located on sapphire crystal or other dielectric material, are uniformly coated with a phosphor, which creates the illusion of a luminous filament. Externally, such lamps are similar to incandescent lamps - they have a transparent glass bulb and there is no plastic in the case.
And so the general design of most LED lamps:
-
basement;
-
plastic or metal case;
-
source of power;
-
metal board with LEDs;
-
light scattering bulb.
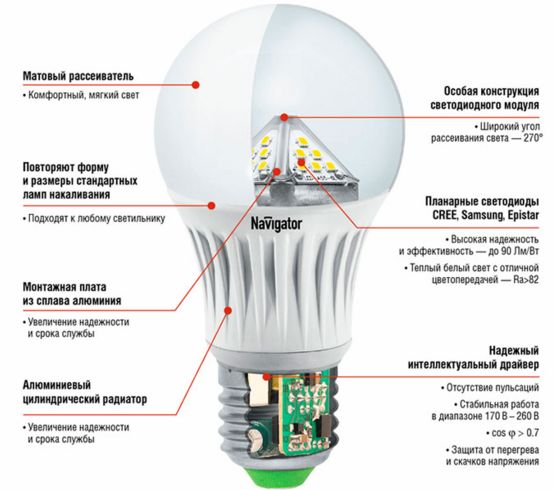
The first difference between luminescent energy savers and LEDs in used light sources: a tube with mercury vapor against semiconductor crystals.
Brightness and power
The lamp has three main characteristics:
-
Power consumption, W;
-
Luminous flux, Lm;
-
Color temperature, K.
In principle, the only possible way to conserve electricity is to increase the specific luminous flux, i.e. Lm / W ratio.
For comparison, let's consider the luminous flux from lamps of different designs:
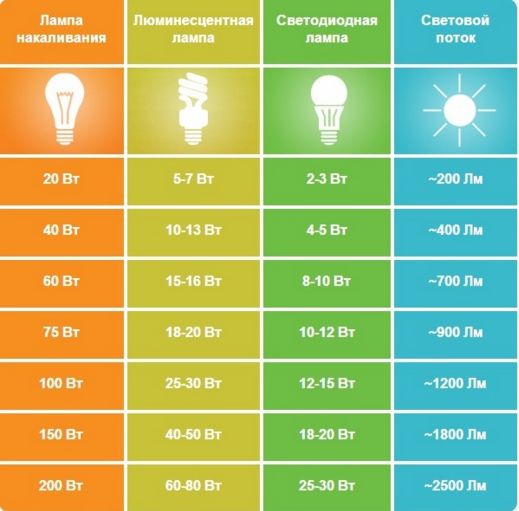
An incandescent lamp, depending on the design features, can produce up to 20 Lm per 1 Watt of power consumption, while most often this is about 10-17 Lm / W.
The fluorescent lamp gives out from 40 to 70 Lm / W. It is worth saying that despite the decline in the popularity of these light sources, engineers improve these indicators and there are publications that about 100 Lm / W are reached, but I have not seen such ones on sale.
LED lamps shine even brighter - 80-120 Lm / W. Over the past decade, this figure has grown significantly, and the price has declined even more.This is the reason for the success of LED products in the market.
It follows that during operation incandescent lamps have the highest heating (more than 100 degrees), energy-saving lamps (60-80 degrees) are in second place, and the coldest lamps are LED (30-40 degrees). This is due to the difference in efficiency, when the LED lamps work, the least amount of energy is released into the heat.
Resource and loss of brightness
30000-50000 hours - the average life of LED lamps. But it greatly depends on the operating conditions. For example, if the LED-light source works in hot conditions, then the period may be reduced by 2 or more times.
10000 - hours work fluorescent lamps. But this is also not a static value, there are cases when they recycle their resources or vice versa - they burn out prematurely.
The main reason for the failure of compact fluorescent lamps is the frequent switching on and off, while those lamps that are turned on around the clock usually experience a resource at times. This is due to the principle of work, more on that later.
The power supply system also affects the length of the operating life. By the way, fluorescent lamps with electromagnetic ballast (inductor) lamps work half as much as with electronic ones. But in compact energy-saving lamps, only electronic ballast (ECG) is used.
1000 hours light bulbs. The service life will be reduced if the lamp is often turned on and off or it operates in conditions with high temperature and vibration. Hitting and shaking the light bulb can damage the spiral and it will break.
Conclusion:
LEDs have the largest resource among the listed analogues. LED lamps are not afraid of frequent turning on and off - this allows them to be used in corridors, toilets and pantries.
Decrease in lamp brightness over time
Incandescent lamps confidently give out their lumens throughout the entire service life, a reduction of up to 7% is possible. The main reason for the decrease in brightness is the contamination of the bulb and the lampshade.
Energy-saving light bulbs, like any type of fluorescent lamp, tend to age. And the luminous flux is reduced to 50% by the end of its life. This is due to the aging of the phosphor, its burnout, wear of the electrodes. You may have noticed that old LLs often blacken at the ends of the tube, this is a sign of an early replacement.
LED lamps give out the declared light stream not constantly. The luminous flux is reduced to 15% after 25,000, which is much longer than that of energy-saving lamps, during this time you will replace two of these, and the LED will continue to work. The brightness also affects the temperature. If the lamp overheats, then the luminous flux drops to 80% of the nominal within 2-3 minutes. With prolonged overheating, the LED crystal degrades and may burn out.
Power way
Both types of lamps require a special approach to nutrition. For this, a power circuit is located inside the case.
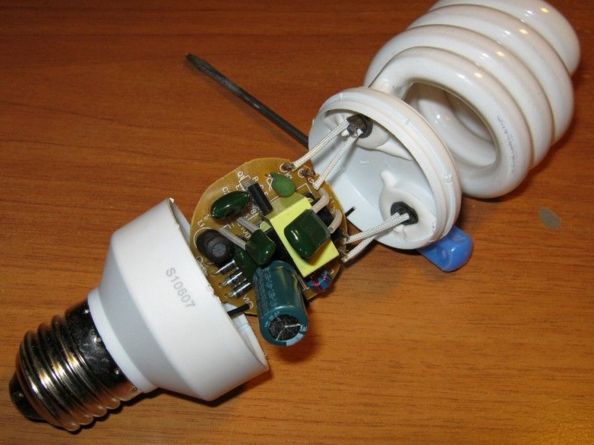
Compact fluorescent tubes
Fluorescent lamps are a rather specific light source in terms of power, to turn them on you need a circuit that increases the voltage above the supply voltage in the mains. Previously, a throttle with a starter was used for this, now an electronic ballast (ballast). Inside the bulb there is gas, at its ends there are two spirals, the voltage is connected to the spirals (electrodes).
To simplify the understanding of the ignition process, I will describe it on the example of an outdated start-up system, in the electronic ballasts used on energy-saving lamps the principle is the same, but the approach is different.
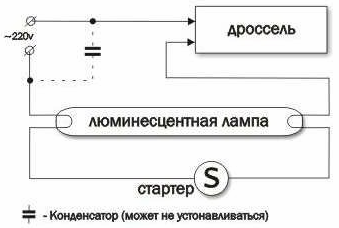
Since in the off (cold) state, the resistance between the electrodes is large, so they are first heated, the starter is responsible for this. A process called “thermionic” emission begins, free electrons begin to be emitted.
In the starter there is a bulb with gas, for example neon, and bimetallic contacts, which in the hot state close and the capacitor.The current is 20-50 mA, the contacts are heated through the gas flask, they close, and the discharge inside the starter flask stops. Then the current limited by the reactance of the inductor and spirals flows along the circuit: Power source - inductor - coil - starter - spiral - power source.
The coils warm up, and the starter plates cool and open. As a result of which, an energy surge occurs sufficient to ionize the gases in the bulb, after which it is ignited, the resistance between the electrodes decreases sharply. These processes lead to the flow of current through the flask and the emission of light.
As you can see, the process is quite complicated. Turning on the lamp is complicated if the spirals are worn out or the phosphor has degraded, as well as in the cold. This is a big problem for all fluorescent, gas-discharge light sources - switching on in frost. It can either take an extremely long time or not turn on at all if the lamp is not of the first freshness. And the resulting brightness in the cold can be lower than the nominal.
Now they are abandoning this approach, using pulsed circuits, which are called electronic ballast or electronic ballasts. You see his typical scheme below. It operates at a high frequency (tens of kHz), against a 50 Hz supply network in a circuit with a choke. This allows you to get a more uniform and bright glow, as well as facilitate ignition of the lamp and reduce electrode wear.
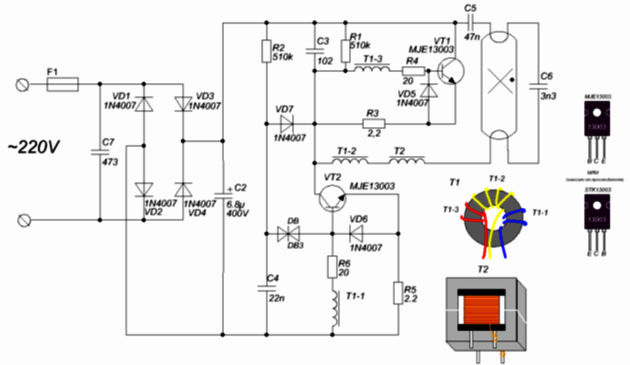

LED lamp
LEDs have simpler power requirements, although they are still quite stringent. The main task is to stabilize the current. The power source is called driver or current source, this is such a device that seeks to maintain a given current regardless of the load resistance. In fact, resistance is limited by driver power.
In the cheapest lamps, there is no driver and stabilization, the current is simply reduced by ballast resistance to an acceptable value, provided the voltage in the mains is normal. But the voltage in the network often deviates from the norm and surges occur, such lamps do not last long, the LEDs burn out due to long work with an increased supply voltage, or during a power surge. A typical ballast driver circuit is shown in the photo.
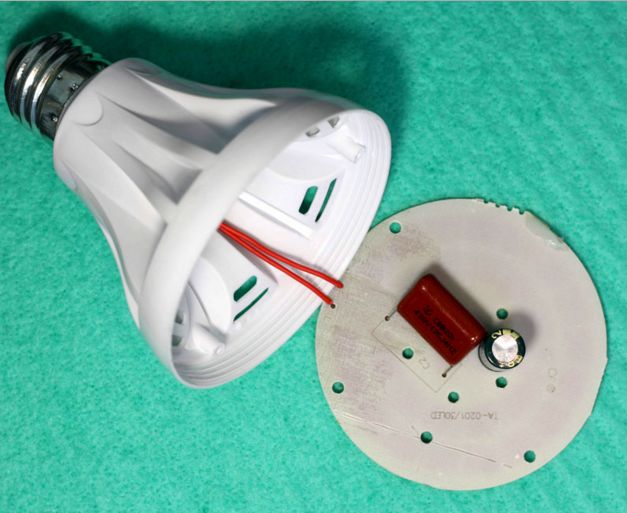
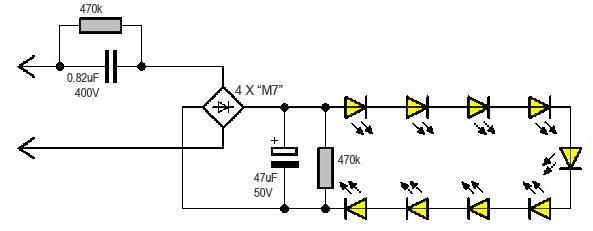

The disadvantages of this scheme are the lack of stabilization and galvanic isolation, protection, the fragility of the lamp, high ripple of the light flux (if a filter capacitor of low capacity is installed).
Advantages - low cost and simplicity.
Recently, however, budget lamps (up to $ 3) with an acceptable pulse driver with current stabilization are often found.
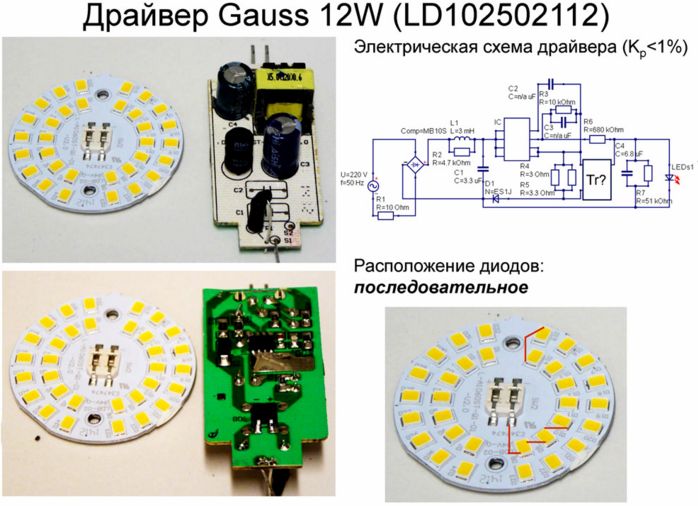
Advantages - galvanic isolation, possible protection, current stabilization, longer LED life, low light ripple.
Disadvantages - the relative high cost, when using low-quality components, the driver can also burn out.
Disposal and environmental damage
The main problem of fluorescent lamps is the use of mercury in a bulb; it harms the environment and human health if it breaks indoors. This causes a large disposal cost (for enterprises). It is necessary to carry out the process of "demercurization".
LED lamps do not harm the environment, can be disposed of as household waste, harmful substances are not used in their manufacture. At the same time, there are companies for their processing for secondary production. There are publications that some enterprises are engaged in the processing of semiconductor crystals.
Conclusion
To summarize and briefly list the advantages and disadvantages of lamps:
Energy Saving Luminescent:
-
"-" The problem of disposal and environmental damage.
-
“-” The luminous flux is lower than that of LEDs.
-
“-” The service life of 10,000, although more than that of incandescent lamps, is less than LED products.
-
"+" Relative reliability.
-
"+" Brightness.
-
"+" Energy consumption.
-
"+" Low operating temperature.
LED light:
-
"-" The price of high-quality lamps can reach up to 8-10 dollars.
-
“-” Low-quality lamps have a poor color spectrum and high ripple.
-
"+" Energy saving.
-
"+" Brightness.
-
"+" Durability.
LED lamps are also energy-saving, but for the reasons mentioned, such a name was attached to compact fluorescent lamps. LEDs are a relevant, reliable and popular light source. Engineers from leading manufacturers are constantly improving the quality of light and the color spectrum.
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
:
