Categories: Featured Articles » Interesting Facts
Number of views: 16250
Comments on the article: 0
Modern wind generators are "preparing" for the reception of wind long before it appears
 The article describes new equipment that allows wind generators to automatically adjust to air flow.
The article describes new equipment that allows wind generators to automatically adjust to air flow.
It would seem that collecting wind energy is a simple matter. Air passes through the turbine blades, causing it to rotate. The turbine drives the generator. A generator produces electricity. But, in fact, not everything is so simple.
Wind generators without fail are installed in the area where storms often rage. A strong wind can damage or even destroy air turbines if they are at the wrong angle. They should be fine-tuned so that powerful gusts rotate, not destroy the blades. Such adjustment is a common thing in working with turbine equipment.
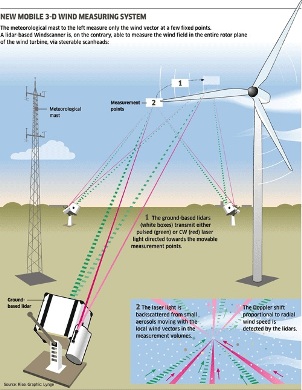
This process can greatly facilitate the technology created Torben Mikkelsen and his colleagues from the Danish National Laboratory of Sustainable Energy Sources Risoe DTU. Dr. Mikkelsen is working on a system that allows each generator to scan upwind and pre-adjust the blades.
Core technology called lidar (LIDAR - the meteorological infrared laser locator) has been known since the 70s. Like the radar, it sends electromagnetic waves, and then analyzes those that returned, determining what they are fighting off from.
The large wavelength of the radar allows you to detect only large objects. The lidar uses light waves. Their length is much shorter and they easily fight off small objects. By the way, human vision is based on light waves. Short waves used in wind lidar, beat off from small particles, such as drops of water, dust, pollen and salt crystals, the movement of which can relatively accurately determine the wind speed.
Dr. Mikkelsen and his colleagues decided that the lidar could scan the impending wind and determine its behavior before contact with the turbine. To test their idea, they installed lidars on 120 meter wind turbines in Hovsor, a Danish training ground for this kind of technology.
Lidars analyzed the approaching wind using a laser that emitted infrared light with a wavelength of 1.55 microns. Stray light was captured by a sensitive device that detects the return of even one photon (the quantum-mechanical particle that makes up the light) from thousands of billions released by the laser.
The device measures the speed of the wind at an altitude of 40, 60, 80 and 100 meters above the ground for 100-200 meters in front of the turbine. Then the collected data is compared with wind measurements with a cup anemometer (which, rotates in the wind, measures its speed) to calibrate the lidar. After that, a computer that analyzes information from the lidar can be connected to motors that adjust the angle of the turbine blades to increase the amount of energy produced and reduce the possibility of damage.
Scientists were able to obtain accurate data at all heights near the turbine. But when installing the device on the ground, a number of problems arose. Directing the laser beam into the air, from the bottom up, he analyzed the ‘cone’ with the starting point at the base of the turbine. So you can calculate the wind speed, but you can not find out how it changes in a 200-meter zone near the generator. To take data, the lidar laser beam should be sent from the center of the air turbine itself.
The installation of a lidar in the center of the wind generator caused difficulties due to the centrifugal force arising from the rotation. For the normal operation of the lidar, the researchers replaced the traditional device, in which the beam is guided by mirrors, a new development with a fiber optic system.
According to Michael Harris, a spokesman for Natural Power, a UK-based wind turbine developer, the center of the turbine is turning into something like a drum dryer. The likelihood that the new device will fail is much less, since in it the light passes through the cable.
Another problem that scientists encountered when installing the lidar is electrical noise from the generator. A sensitive detector may deviate under the influence of stray currents. Researchers have suggested wrapping the lidar in a protective material that ground excess energy.
The result is a system that improves electricity production by 5%. Maybe the figure is not impressive, but for one turbine with a capacity of 4 megawatts, the savings are 38,000 dollars. in year. Do not forget about increasing the service life of the blades and the generator itself.
See also: Inpower generators in Russia: how to choose, install and avoid disappointment
See also at bgv.electricianexp.com
: